Warm Up
100 likes | 224 Views
This comprehensive guide covers the calculation of the sum of multiples of 7 from 11 to 391, along with solving for terms and sums in various arithmetic and geometric sequences. It explores convergence and divergence in sequences, providing examples of both types. With given values for sequences, you'll learn to determine sum formulas and analyze whether sequences converge toward a limit or diverge. Engage in discussions about sequences, and practice identifying numerous sequence behaviors with real-number implications. Ideal for students and educators alike.

Warm Up
E N D
Presentation Transcript
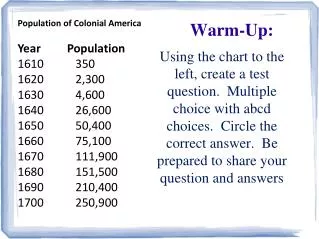
Warm Up Calculate the sum of the multiples of 7 between 11 and 391. For an arithmetic sequence, A1=56 and A11=-14. Determine S15. For a geometric sequence, A1=125, and r = -2/5. Determine S5. For a geometric sequence, A1=16, r =3/2, and Sn =211. Determine n and An.
Convergent: A sequence converges if as n increases without bound, the terms of the sequence get closer and closer to some real number (called the limit). Divergent: Any sequence that does not converge.
Determine whether the sequence will converge or diverge. 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, …. 2, 0, -2, 0, 2, …. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ….
Discuss with your group… • Write an example of an arithmetic sequence that will diverge. • Write an example of an arithmetic sequence that will converge. • Find an example of an geometric sequence that will diverge. • Find an example of an geometric sequence that will converge.
Infinite geometric series… Determine whether the sequence will converge. If it converges, calculate the sum.
Infinite geometric series… Determine whether the sequence will converge. If it converges, calculate the sum.