Introduction to Tissues: Types and Functions
260 likes | 278 Views
This text provides an overview of tissues, including the four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. It focuses on epithelial tissue, its structure, functions, and special properties. Additionally, it covers the classification of epithelium based on cell layers and shapes, as well as glandular epithelium and exocrine glands.

Introduction to Tissues: Types and Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
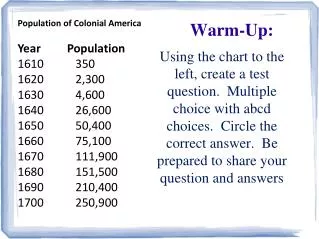
Warm-Up • What is a tissue? • The study of tissues is called ______. • What are the 4 main types of tissues? (See the intro to Chapter 4 in textbook)
Warm-Up What type of epithelial cell is shown below? 1. 2. Simple Columnar Epithelium Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium 3. 4. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric
Tissue: group of cells that are similar in structure and function • Histology: study of tissues Types of Tissues: • Epithelium (covering) • Connective (support) • Muscle (movement) • Nervous (control)
Preparing tissues for microscopy • Specimen is fixed (preserved) • Cut into thin sections (slices) • Stained with colored dyes
Epithelial Tissue • “epithe” = laid on, covering • Structure: • Covering and lining epithelium • Glandular epithelium • Function: • Protection • Absorption • Filtration • Secretion
Special Properties • Polarity • Apical surface = exposed free surface or edge (some with microvilli, cilia) • Basal surface = lower, attached surface • Specialized contacts • Fits close together to form continuous sheets
Special Properties • Supported by connective tissue • Rests on basement membrane • No blood supply (avascular) • Rely on diffusion and underlying connective tissue for food/O2 • Regeneration – Replace lost cells
Classification • Two names = (# cell layers) + (shape of cells) • Cell Layers: simple or stratified • Shapes: squamous, cuboidal, or columnar
Simple Epithelium • Absorption, secretion, filtration • Very thin
Simple Epithelium • Simple squamous • Filtration, rapid diffusion • Capillary walls, air sacs in lungs, kidney filtration • Serous membranes: slick layer lining ventral body cavity and its organs
Simple Epithelium • Simple cuboidal • Secretion & absorption • Lines ducts of glands (salivary), kidney tubules, ovary surface
Simple Epithelium • Simple columnar • Absorption and secretion • Lines digestive tract • Microvilli, cilia • Mucous membranes: lubricating mucus
Simple Epithelium • Pseudostratified columnar • Rests on basement membrane – false impression (pseudo) of being multi-layered • Secretes or absorbs • Respiratory tract – cilia propels mucus from lungs
Stratified Epithelium • 2+ layers, more durable • Main function = protect
Stratified Epithelium • Stratified squamous • Withstand abuse, friction • Esophagus, mouth, outer portion of skin
Stratified Epithelium • Stratified cuboidal • Usually 2 layers • Mainly in ducts of large glands (sweat, mammary, salivary) Sweat Gland Esophageal Gland
Stratified Epithelium • Stratified columnar • Thick, waterproof layer • Pharynx, male urethra, lining ducts
Transitional Epithelium • Able to change shape (cuboidal squamous) • Lining of hollow urinary organs (bladder, ureter, urethra) • Stretches when filled with urine
Glandular Epithelium • Gland: make and secrete a particular product • 2 Types: • Endocrine gland: produce hormones secreted into tissue fluid or bloodstream • Exocrine gland: secrete products into ducts onto body surfaces or body cavities • Eg. mucous, sweat, oil, saliva, bile
Exocrine Glands Unicellular Multicellular • Mucus cells or goblet cells • Duct structure