Exploring the Plant Kingdom: Characteristics, Evolution, and Types of Plants
140 likes | 269 Views
The Plant Kingdom consists of eukaryotic, multicellular organisms that are primarily autotrophic, using sunlight for photosynthesis. Key features include cellulose in cell walls and sexual reproduction. Plants evolved from green algae around 475 million years ago and made the transition to land. They exhibit alternation of generations with diploid sporophytes and haploid gametophytes. There are four main types of plants: non-vascular, vascular seedless, gymnosperms, and angiosperms, each with distinct characteristics. Plants are essential for agriculture, providing food, materials, and environmental benefits.

Exploring the Plant Kingdom: Characteristics, Evolution, and Types of Plants
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Characteristics • Eukaryotic • Autotrophic • Multicellular • Sexual reproduction • Cellulose in cell walls
Need to survive… • Sunlight – role in photosynthesis • Gas exchange – Oxygen/carbon dioxide • Water and minerals – symbiotic relationship???
History • Thought to evolve from Green algae, presently classified as a Protist • May be moved to plant kingdom due to cellulose in cells walls and pigment, similar life cycles and their genome • 475mya – move to land • Small, non vascular, needed water to reproduce
Life cycle • Alternation of generations – has 2 alternating phases • Diploid (2n) – Sporophyte – spore producing plant • Haploid (n) – gametophyte – gamete producing plant
4 types of plants • Non-vascular • Vascular seedless • Gymnosperms (naked seed) • Angiosperms (flowering plants)
Non –vascular - Bryophytes • No true roots, stems or leaves • Water (green algae) and land (mosses) • Bryophytes have a protected embryo • lack vascular system – why they are small • Gametophyte is dominant generation • Archegonia – eggs • Antheridia - sperm
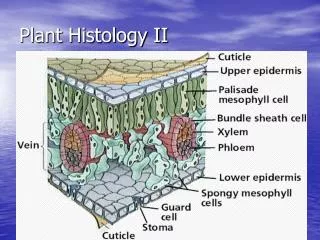
Vascular seedless • 2 types of vascular tissue • Xylem – transports water and minerals • Phloem – transports food • Sporophyte dominant • Examples - ferns
Gymnosperms – seed plants • Seed – plant embryo and a food supply • Pollen grain – where male gametophyte is contained • Carried by wind, animals • Seed coat – surrounds and protects the embryo, keeps from drying out.
Angiosperms – flowering plants • Advantage – helps to attract animals and insects to increase reproduction. • Fruits – structure containing 1 or more matured ovaries • Eating of fruits by animals help to disperse seeds for growth
Classification of angiosperms • Monocots • Single cotyledon • Parallel veins • Flower parts in multiples of 3 • Dicots • Two cotyledon • Branched veins • Flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5
Plants and Humans • Benefits: • Agriculture, food • Clothing, fibers • Wood, construction • Keep the environment clean and green!! • Harmful: toxins, poisons, allergies