Mitosis
200 likes | 568 Views
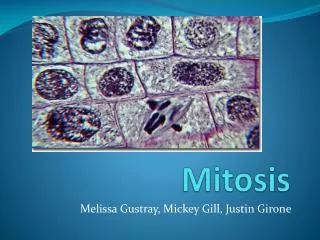
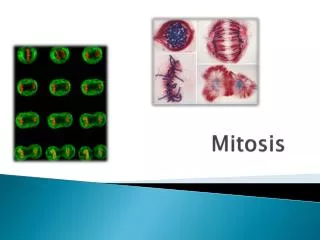
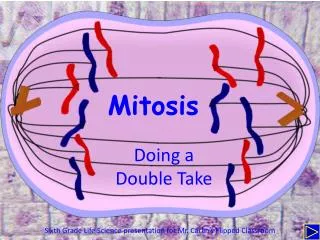
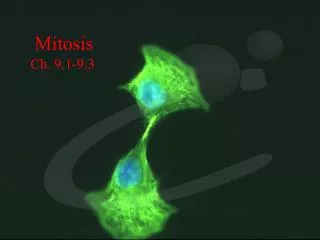
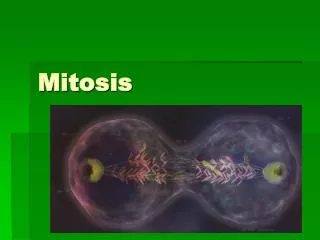
Mitosis. Mitosis. The process in which cells divide to enable growth and to replace worn or injured cells. . Mitosis. The process in which cells divide to enable growth and to replace worn or injured cells.

Mitosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mitosis • The process in which cells divide to enable growth and to replace worn or injured cells.
Mitosis • The process in which cells divide to enable growth and to replace worn or injured cells. • Mitosis produces TWO daughter cells GENETICALLY IDENTICAL to their parent cells so the same cell functions and process continues.
Mitosis • The process in which cells divide to enable growth and to replace worn or injured cells. • Mitosis produces TWO daughter cells GENETICALLY IDENTICAL to their parent cells so the same cell functions and process continues.
Phases • Interphase – chromosomes replicate. A chromosome and its copy are called chromatids.
Phases 2. Prophase – Chromosomes shorten and thicken. Nuclear membrane disappears. Chromatids held together at centromere. Spindle fibres develop from the centriole.
Phases 3. Metaphase – The spindle fibres twist and turn the chromatids, lining them up along the equator.
Phases • 4. Anaphase – the centromeres split and individual chromatids move towards the poles; pulled by the spindle fibres.
Phases • 5. Telophase – chromatids arrive at the poles. Nuclear membranes begin to form around each group.
Phases 6. Cytokenesis - The cell cleaves, and two daughter cells are formed; each with exactly the same number of chromosomes. Each cell has identical genetics information. The daughter cells will grow and repeat the whole process.
Mitosis • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DD3IQknCEdc&feature=related