Gel Electrophoresis
190 likes | 598 Views
Gel Electrophoresis. First, What……. Simply put, gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate molecules such a DNA, RNA and proteins according to size. Requires an electric current as these molecules are negatively charged

Gel Electrophoresis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
First, What…… • Simply put, gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate molecules such a DNA, RNA and proteins according to size. • Requires an electric current as these molecules are negatively charged • We’ll be looking at separating long strands of DNA into smaller fragments. • Can be used to determine someone’s DNA identity (fingerprint), assign paternity, ID criminals from a crime scene, determine relatedness among individuals, useful in cataloging endangered species
First, DNA is Extracted • The same DNA is found in the nucleus of nearly all of your cells (mature red blood cells have no nucleus). • Mitochondrion have a totally different set of genes than what is in the nucleus. You inherit them from your mother! Many studies use this DNA to determine how closely related different species of organisms are! • Nuclear DNA can be extracted from blood, cheek cells, hair follicles, tooth pulp or mostly any other tissue • There are quite a few protocols that use a variety of chemicals and buffers to isolate ONLY DNA and get rid of everything else
Restriction Enzymes • Long strands of DNA, usually from those regions that do not code for anything, are cut into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes • Each enzyme recognizes different sites to cut • This results in many fragments of different sizes (number of bases long)
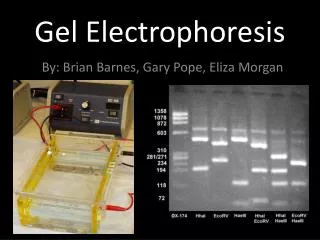
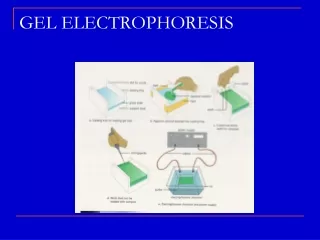
Prepare for gel electrophoresis After the gel cools and becomes jelly-like, the comb is removed and is placed in the chamber filled with buffer Power supply A compound called agarose is melted in a buffer, poured into a mold and a tooth comb inserted to create wells Gel Chamber with buffer
“running a gel” A loading dye (seen in blue) is mixed with DNA sample and loaded into a well Electrical supply is turned on…DNA fragments run through the gel from the negative electrodes toward the positive DNA Ladder (or size standard) is also loaded. This lets allows you to determine how long each fragment is (in kilobases) The gel is stained and examined. The smallest (shortest) fragments travel the farthest down the gel
Example of Fingerprints Out of the 7 suspects, the bloodstain found at the scene of the crime belongs to……..
A person should have ½ of their DNA fragments from their mother, and ½ from their father. **Below: known mom, child and 3 alleged fathers Mom Child AF1 AF3 AF2 The child received these fragments from its mother… - …So Alleged Father #2 is the father of the child. ..which means that they must have received these from the father… …so, which alleged father has the same size fragments as the child at these positions??? +