SPONGE
220 likes | 360 Views
Body Systems, Day 1. SPONGE. Which muscle do you think is the most important? Explain why in a sentence. How can you keep your muscles healthy?. Body Systems and Exercise. Section 1: The Muscular System. The Muscular System.

SPONGE
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Body Systems, Day 1 SPONGE Which muscle do you think is the most important? Explain why in a sentence. How can you keep your muscles healthy?
Body Systems and Exercise Section 1: The Muscular System
The Muscular System • There are more than 600 muscles in the body, providing motion and maintaining posture. • Muscles are divided into 3 major groups:
Skeletal Muscle • Skeletal, or voluntary muscle, is muscle that a person can control. • These muscles are mostly located in the arms, legs and outside the bones of your body.
Smooth Muscle • Smooth, or involuntary muscle, functions without a person thinking about it. • For example, your stomach and intestinal muscles move food throughout your body without you thinking about it.
Cardiac Muscle • Cardiac muscle is located only in the heart. It looks like skeletal muscle, but is not voluntary. • This muscle contracts steadily to keep your heart beating, but can speed up for exercise and emergencies.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WRxsOMenNQM&NR=1 Inside the Muscle Fiber • There are many parts of a muscle fiber, but two main parts are involved in flexing: • Myosin has “arms” that grab and climb, causing the muscle to contract. • Actin acts as a ladder for myosin to climb up.
Adenosine Phosphate Phosphate Phosphate What Makes Muscles Move? • Muscles use energy in the form of ATP molecules to contract. • ATP is short for Adenosine triphosphate • ATP is a molecule made up of Adenosine and 3 phosphates.
ATP Becomes Energy • When an ATP molecule is broken, energy is released and used for muscles to move. • With only two phosphates left, ATP becomes ADP. Adenosine Energy Phosphate Phosphate Phosphate
Free Radicals • When you exercise, your muscles break apart many ATP molecules into ADP. • All of the extra phosphates, known as Free Radicals, float around in the tissues and damage muscle. • Fortunately, your body has ways of preventing the spread of free radicals.
Adenosine Phosphate Phosphate Removing Free Radicals Phosphate Free Radical • There are two ways the body can get rid of free radicals. • During exercise, your body pumps Lactic Acid into the bloodstream. • The Lactic Acid reconnects the Free Radicals to the ADP, turning it back into ATP. Now the body won’t be harmed and it will have more energy. Lactic Acid
Antioxidants • Antioxidants also bind to free radicals, making them harmless to the body. • Antioxidants can be found in colorful fruits like blueberries and strawberries, as well as many types of beans. • People, especially athletes, should eat food rich in antioxidants because they produce more free radicals during exercise.
Major Muscle Groups 1 Deltoids 2 Pectorals 3 Biceps 4 Abdominals 5 Quadriceps Abdominals Biceps Deltoids Pectorals Quadriceps
Major Muscle Groups 1 Traps Gastrocnemius 2 Triceps 3 Lats Glutes Hamstrings Glutes 4 Lats Hamstrings 5 Traps Triceps 6 Gastrocnemius
Flexors and Extensors • Muscles work in pairs called flexors and extensors. • Flexors bend an arm or a leg. • Extensors straighten the limb back out. • Remember though, both muscles can only shorten.
Caring for your Muscles • To build muscle, you can eat protein but give yourself time between workouts to rest so the muscles can build up. • Eat carbohydrates to fuel muscle. • Train your muscles aerobically (more than 15 minutes in a row) to build muscle tone and train your heart.
Muscles and Exercise • There are two basic muscle types involved in exercise: • Fast twitch muscles: Contract quickly for fast, strong movements, but tire quickly. • Slow twitch muscles: Contract more slowly, but can exercise for much longer. • You are born with a certain number of fast and slow twitch muscles, and cannot grow new ones. You can exercise them to make them work better.
Exercise in Junior High • Female muscle strength will gradually grow in the teen years, while male muscle will grow up to 10 times. • Strength training will benefit young teen athletes, but only if done correctly.
Exercise in Junior High • The connections between your bones and muscles do not finish forming until high school. Lifting large amounts of weight in 8th grade can seriously damage your joints and affect your growth plates. • Young teens should lift smaller amounts of weight many times. (6 - 15 reps for each muscle group) • Lift no more than 3 – 4 times a week for about 30 – 60 minutes. • Increase the maximum weight you lift no more than 5 -10 pounds from day to day.
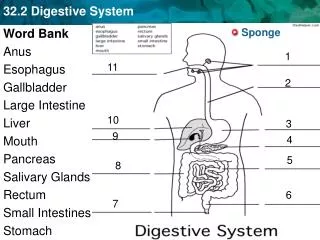
Unit Project • In groups of two, create a life-sized drawing of a body system. Each group chooses one of the following body systems: • Muscular • Nervous • Digestive • Skeletal • Circulatory • Respiratory
Unit Project • Once you have chosen a system: • Use the provided diagram as a guide • Use markers to color body parts • Label body parts • Projects are due on the day of the health test and worth 20 points