The Respiratory System
140 likes | 209 Views
The Respiratory System. Alex Sgro Santina Marinelli Steve Cofrancesco Briana Tosado. Functions. The primary function is to obtain O₂ Removes CO₂ E ntraps particles from incoming air to control water temperature and content T ransports air into and out of the lungs.

The Respiratory System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Respiratory System Alex Sgro SantinaMarinelli Steve Cofrancesco Briana Tosado
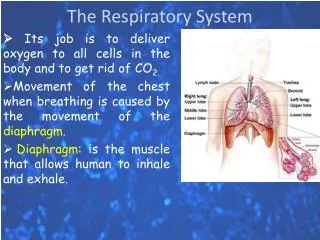
Functions • The primary function is to obtain O₂ • Removes CO₂ • Entraps particles from incoming air to control water temperature and content • Transports air into and out of the lungs
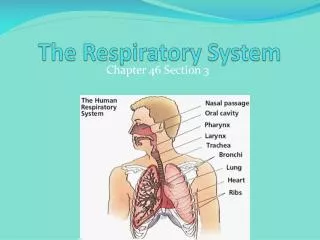
Organs of the Respiratory System • Upper respiratory tract: • Nose • Naval cavity • Paranasal sinuses • Pharynx • Lower respiratory tract: • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchial tree • Lungs
Nose • Supported by bones and cartilage internally • Air enters/leaves through two nostrils • Nostrils guarded by hairs, which prevent entry of large particles in the air
Nasal Cavity • A hollow space behind the nose • The nasal septum divides the nasal cavity into right and left portions • Nasal Conchae divide the cavity into passageways • Mucous membrane lines the cavity • Adjusts the temp. of the air to that of the body and entraps particles from air.
Paranasal Sinuses • Air filled spaces within the skull and opening into the nasal cavity. • Mucous Membrane line the sinuses. • Reduce the weight of the skull and affect quality of sound.
Pharynx • Also known as the throat • Passageway for food and air • Produces sounds of speech
Larynx • Conducts air in and out of trachea and prevents foreign objects from entering. • Houses the vocal cords • Tension on vocal cords controls pitch
Trachea • Also known as the windpipe • Ciliated mucous membrane lines the inner wall • Filters the air and entraps particles • Hyaline Cartilage prevent Trachea from collapsing and blocking the airway
Bronchial Tree • Branched airways leading from trachea to air sacs. • Branches begin with 2 primary bronchi which continue to break into smaller and smaller branches. • Smaller tubes=bronchioles • Smallest tubes=alveolar ducts • Alveolar ducts alveolar sacs alveoli
Lungs • Soft, spongy, cone-shaped organs in thoracic cavity. • Enclosed by diaphragm and thoracic cage and medially separated by the mediastinum. • The visceral pleura attaches lungs and folds to become parietal pleura, which forms mediastinum. • The space in between the visceral pleura and parietal pleura is called the pleural cavity.
Ventilation • Also known as breathing • Normal Air pressure: 760 mm of Mercury • Movement of air in and out of body • Based on pressure and volume • 2 parts of process • Inspiration • Expiration
Inspiration (Inhaling) • Air pressure low • The diaphragm contracts downward • Rib muscles pull upwards • Thoracic cavity increases in size • Air rushes in to fill lungs
Expiration (Exhaling) • Air pressure high • Elastic recoil of tissues • Surface tension • Diaphragm relaxes • Thoracic cavity decreases in size • Lungs contract and expel air • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rPKyoD4Jkoc