Earthquakes: Origins, Waves, and Hazards
210 likes | 236 Views
Explore the science behind earthquakes, including their origins, different types of waves, measurement techniques, and associated hazards like liquefaction, aftershocks, and tsunamis. Discover the shadow zone and learn how waves bend and slow when passing through Earth's liquid layer.

Earthquakes: Origins, Waves, and Hazards
E N D
Presentation Transcript
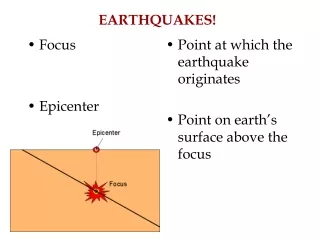
Focus Epicenter Point at which the earthquake originates Point on earth’s surface above the focus EARTHQUAKES!
Earthquake Where do earthquakes occur? The shaking of Earth’s crust due to the release of built-up pressure and stress Usually at plate boundaries but also at small faults WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE?
P waves S waves L waves Primary; compressional; travel through solid, liquid and gas; FASTEST! Secondary; shear; only travel through solids; 2nd fastest Surface waves; very slow Earthquakes Waves
Seismograph Seismometer Record sheet that the seismometer produces Measures earthquake waves Measuring Earthquakes
Need information from at least 3 seismograph stations Locating Earthquakes Epicenters
Magnitude Richter Scale Strength of the Earthquakes Measure the magnitude of earthquakes……ranges from 1-10 Strength of Earthquakes
Liquefaction Aftershocks tsunamis Liquid characteristics Tremors after the main earthquake has passed; just as dangerous! Undersea earthquakes that spark large, rogue waves Earthquake Hazards
Shadow Zone Moho Area that receives no earthquake waves do to Earth’s liquid layer (outer core) Bending of Earthquakes waves and they slow when they pass through the liquid astehenosphere The Shadow Zone