Biomes
350 likes | 942 Views
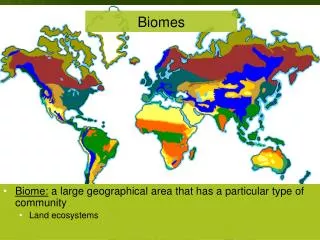
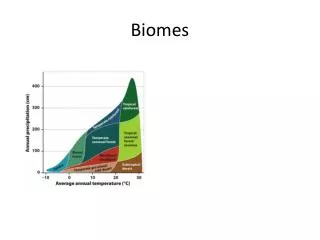
Biomes. a Dr. Production. IV. Terrestrial Biomes (life zones). A. Def. - geographical areas distinguished by particular dominant flora B. Characteristics 1. Not a place, but a class of plants 2. Determined by climate 3. Boundaries are indistinct

Biomes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biomes a Dr. Production
IV. Terrestrial Biomes (life zones) • A. Def. - geographical areas distinguished by particular dominant flora • B. Characteristics 1. Not a place, but a class of plants 2. Determined by climate 3. Boundaries are indistinct 4. Convergent evolution common between similar biomes • Plant Adaptations Brain Pop Land Biomes (dekalbcs dekalb)
V. Marine & Aquatic Biomes • Primary ecological subdivisions of organisms 1. Plankton - at mercy of currents, weak or nonswimmers (small or microscopic) a. Phytoplankton - primary producers, (cyanobacteria or diatoms) b. Zooplankton - protists and small animals (larval stages) 2. Benthos - bottom dwellers (sessile, walking, or burrowing) 3. Nekton - larger, strong swimmers (top of the food chains)
B. Freshwater 1. Zones a. Littoral zone - near shoreline, richest in life b. Limnetic zone - open water, sparse life c. Profundal zone - deep. anaerobic, no light, detritovores, mineral rich
3. Types of lakes a. Oligotrophic - nutrient-poor, deep, sandy or rocky bottom, clear b. Eutrophic- nutrient-rich, phytoplankton very productive, shallow, murky Oligotrophic lake Eutrophic lake Eutrophication (lake aging)
Marine life zones 1. Estuaries and salt marshes - where rivers (freshwater) meets saltwater of ocean - most fertile water in the world, breeding grounds for many fish, nutrients from rivers meets constant mixing of tides (plants)
2. Intertidal zone- between high and low tides, rich in life forms (barnacles, clams, crabs), tidal pools 3. Subtidal zone - sea stars, sea urchins, worms, crabs, flounder 4. Neritic zone - over continental shelf (nekton and most benthic organisms are here (food is here) [photosynthetic limit - 200 meters] 5. Pelagic zone– includes neritic and open ocean 6. Benthic zone- deep waters, mostly predators
= Neritic zone • (Neritic zone)
Abyssal Zones 1. The mid-ocean ridge system with well known deep-water hydrothermal vent (ellipses) and cold seep (oblongs) regions. Vents: 1, Mid-Atlantic Ridge; 2, East Pacific Rise; 3, Galapagos Rift; 4, NE Pacific; 5 and 6, W Pacific back-arc spreading centres; 7, Central Indian Ridge. Cold seeps: 1, Gulf of Mexico; 2, NW Africa; 3, Laurentian Fan; 4, Barbados accretionary prism; 5, Monterey Bay; 6, Oregon subduction zone; 7, Sagami bay.
Biomes Resources • Biome Interactive Movie • Biomes of the World Videos • Planet Earth: Ice Worlds: Oasis of Rock • Essential & Endangered: Coral Reef Biomes • Plant Adaptations