Fungi
90 likes | 264 Views
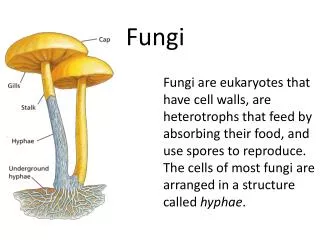
Fungi. 7th Grade Science. What are fungi?. Molds Mushrooms Mildews Yeast Unicellular and multicellular Shared characteristics Eukaryotes Use spores to reproduce Heterotrophs Need moist, warm places to grow. Cellular Organization. Cells are arranged in structures called hyphae

Fungi
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fungi 7th Grade Science
What are fungi? • Molds • Mushrooms • Mildews • Yeast • Unicellular and multicellular • Shared characteristics • Eukaryotes • Use spores to reproduce • Heterotrophs • Need moist, warm places to grow
Cellular Organization • Cells are arranged in structures called hyphae • Hyphae are branching, threadlike tubes • Substances move quickly through hyphae • Appearance of fungus depends on hyphae arrangement
Obtaining Food • 1st - fungus grows hyphae into food source • 2nd - digestive chemicals ooze from tips of hyphae into the food • 3rd - digestive chemicals break down the food into small substances that the fungus can absorb through its hyphae
Reproduction • Fungi produce lightweight spores in fruiting bodies • Fruiting bodies = reproductive hyphae • Spores are surrounded by a protective covering • Spores can be carried easily by air or water to new sites • Fungi produce many more spores than will ever grow into new fungi
Classification of Fungi • Classified based on shape of spore-producing structures and on ability to reproduce sexually • 4 groups of fungi • Threadlike fungi (600 mold species) • Sac fungi (30,000 species – yeast, morels, truffles, disease-causing fungi) • Club fungi (25,000 species – mushrooms, plant parasites) • Imperfect fungi (25,000 species that do not reproduce sexually)
The Fungus Among Us!!! • Fungi are decomposers • Break down dead plant and animal matter • Many provide food for people • Yeast in bread and wine • Blue cheese and mushrooms • Some cause disease • Athlete’s foot, corn smut, wheat rust, ringworm • Some fight disease • Penicillium discovery lead to penicillin • Some fungi live in symbiosis with other organisms • Help plants grow larger and healthier – hyphae help absorb water and nutrients
Lichens • Lichen is a fungus and either algae or bacteria that live together • “Fred Fungus to a lichen to Alice Algae” • Lichens are irregular, flat, crusty patches that grow on tree bark or rock • Fungus benefits from food produced by algae/bacteria, algae/bacteria obtains water and minerals from the fungus