Warm up- copy and answer
170 likes | 502 Views
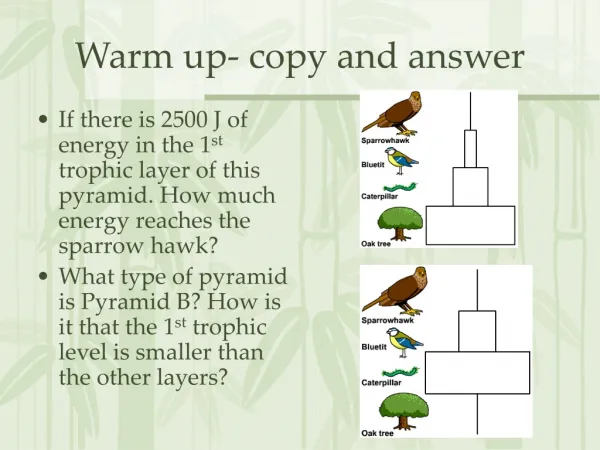
Warm up- copy and answer. If there is 2500 J of energy in the 1 st trophic layer of this pyramid. How much energy reaches the sparrow hawk? What type of pyramid is Pyramid B? How is it that the 1 st trophic level is smaller than the other layers?. Species Interactions.

Warm up- copy and answer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm up- copy and answer • If there is 2500 J of energy in the 1st trophic layer of this pyramid. How much energy reaches the sparrow hawk? • What type of pyramid is Pyramid B? How is it that the 1st trophic level is smaller than the other layers?
What Shapes an Ecosystem? • Biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving ) factors. • Habitat- Area in which an organism lives. • Niche • Species interactions
What is a Niche? • Niche- • the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives. • The way the organism uses those conditions.
What is a niche? • Includes: • Physical conditions in which the organism lives. • Habitat. • Temperature ranges. • Position in food web. • Food choices • Reproductive strategy
Species Interactions • Interactions between populations within a community can greatly affect an ecosystem. • Symbiosis • Predation • Competition • Inhibition
Symbiosis • When two species live together: • Mutualism • Parasitism • Commensalism
Symbiosis • Mutualism- two species provide resources or services to each other • Both benefit.
Symbiosis • Mutualism- benefit usually in –nutrition, transportation, protection Acacia Ant Clown Fish- Anemone
Symbiosis • Parasitism- One organism feeds on another • Benefits parasite • Harms host Tapeworm Roundworm Heartworm
Commensalism • One species benefits from another • Enhances fitness of one species • No effect on other species Epiphyte
Predation • Predation- one species feeds on another • Carnivores- kill and eat one prey • Herbivores- remove and eats parts of many prey, rarely lethal • Parasites- consume nutrients from one prey, rarely lethal
Competition • Competition- two species require the same limited resource in an environment. • Can harm one or both species
Competition • Interspecific competition- between members of different species • Intraspecific competition- between members of the same species
Competition • Competitive exclusion principle- • If two species occupy the same niche, the stronger competitor will eliminate the competitor. • Weaker competitor leaves niche or becomes extinct