The Yanomamo: Guardians of the Amazon
340 likes | 474 Views
The Yanomamo, one of the world's oldest and most isolated cultures, inhabit the Amazon region on the borders of Brazil and Venezuela. Their existence remained largely unknown until the 20th century, when outside contact began with missionaries and later, gold miners. This contact has brought disease, violence, and environmental destruction, threatening their way of life. Despite these challenges, the Yanomamo sustain their rich cultural heritage through traditional farming and hunting practices, maintaining a deep spiritual connection with their environment and its resources.

The Yanomamo: Guardians of the Amazon
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Yanomamo The Fierce People
History • One of the oldest and last remaining ancient cultures in the world • Their existence wasn't really known to the world until the 20th century • 1940-1960 first missionaries • got infected with an illness that caused many deaths • 1970-1980constant compact with the regional border by development projects, large losses • 1980, rich mineral stores were discovered, gold diggers came • 1993, Haximu massaccre where 16 people of the Yanomami were killed by Gold Diggers
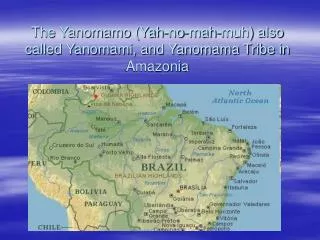
Location In the Amazon region of Venzuela and Brazil Tropical Rainforest of Northern Amazonia on the border between Brazil and Venezuela (Ornico-Amazon interfluvial region where there is fertile land near the Amazon river) Past Location: Headwaters of Parima and Orinoco Rivers Parima Mountain range and the watershed between the upper orinoco and right bank affluents of Rio Branco t
Climate • Very warm climate • During the rainy season it is humid
Migration of Culture • Migrated across the Bering Straits between Asia and America some 40,000 years ago making their way slowly down to South America • Inhabited the region of Orinoco and Parima Rivers for the past 1,000 years • Past 700 years, split into subgroups and developed different languages • In the Early 1800's migrated from Parima mountain regions to nearby lowlands • Considered "Primitive" because they have not discovered wheels and metals • Isolated Culture, haven't really spread around much • Missionaries have come in hopes of converting them to Christianity, others have come introducing them to new technologies but it hasn't worked • Live in their own little world, best for them
Resources • Rainforest plants are rich in secondary metabolites, particularly alkaloids • At least 3000 fruits are found in the rainforests; of these only 200 are now in use in the Western World. The Indians of the rainforest use over 2,000 • One-fifth of the world's fresh water is in the Amazon Basin. • Fertile Land for growing crops, diverse wildelife
Economic Lifestyle • Hunter-Horticulturalists • Hunter because they hunt • Horticulturalists because they have an advanced knowledge on crops and gardening • Also may use slash and burn technique to clear gardens and nurture growing seeds • Trade is important among tribes for acquire basic resources and distribute surplus items, also trade for political reasons to form alliances • Trading items include recreational drugs, cotton, tobacco
Decline or Rising Status • Stagnant/slow decline • 1,000 goldminers are working on thier land illegally • Cattle Rancher's are invading and deforestating the eastern fringe of land • malria, polluting rivers with mercury • Survival efforts are there
Government • Leadership determines' the village's relationship with other villages • The result of kinship/marriage • Leaders "big men" come from the largest kinship; do not recognize Chiefs • Consider males more important/powerful than women • Clear Gardens, plant crops, collect wild foods and hunt • Leaders are peace makers/warriors, referred to as fierce because peirce making takes forcefulness
Relationships Relationships between groups are maintained through alliance and warfare In this patrilineage, fellow lineage members are close relative, call each other brother and sister If they aren't as close may develop hostile relationships which results in segmentation of the village which forms new settlements People may be tied together by affinal ties or consanguine ties ( house/village) Settlements not linked by marriage or divided by way invite each other to elaborate feasts which includes gifts of Exogamy rare, usually for military alliances Marriages not for love
Culture Neo Indians with Culture that date backs to 8,000 years Descendants of an indigenous group that had remained isolated for a remote period of time Populations kept dispersing, process of internal differentiation, forming new languages Each community is independent from each other Descisions are made my a consensus Consider women to be inferior, male dominant Men hunt for prey, women tend the gardens Mutifamily houses called shabanos/Yano (in the shape of a cone)Each collective village an autonomous economic/political entity Approxamately 200-250 villages, about 40-350 in one village
Culture Daily Life includes: gardening, collecting firewood, making crafts, fetching water, gossiping/visiting with eachother
Contributions to Society/World • Have not made and significant contribution the the world other than being a topic of study • Research their diets because they have high potassium levels
Religion/Belief System • Practice Animism (every creature, rock, tree, mountain has a spirit) • Shaman's control these spirits by inhaling a hallucinogenic material. Inhaling the hallucinogen gives the shaman the power to control these spirits or Xapripe Davi Kapenawa • Believe there is a God called Omama, who blessed them with forest, trees and animals • Believe that animals were once humans to but were made animals because of the bad things they did • Men become Shaman's, main job is to heal the sick. Ironically, they also believe that illness is called by the shaman who is making the hekura, or spirit sicken the body • Training period with food depravation and abstinence from sex • Pull the demon out with the help of his own demons
Religion/Belief system • Cosmos consist of 4 layers • The top layer is empty but was once occupied by ancient beings duku ka misi • Second Layer (sky)) contain spirits of dead men and women It resembles earth but everything is better hedu ka mis • Third Layer is the earth hei ka mis • The fourth layer is the underworld hei ta bebi • The Amahi Teri are spirits who live in the underworld and cause misfortune to humans
Music/Literature/Art • Pass information orally, not from writing • Play on words, chanting, myth telling, story telling to preserve thier history and entertain themselves • No Musical instruments, women sing • Drawing and paintings • Sparse geometric designs, bold symbols, black/red, adorn common objects such as pots
Clothing • Men wear little more than string around thier waist, it is is a clear indication that a boy has become a man when he does that • Women use cotton and yarn to make clothing, also make waistbands but it covers close to nothing • Halter neck adornaments • Feathers may be worn on the head upper arm or earlobes; express the relationship between man an animal, social status, personality, etc
Customs (Marriage) • Older kin, usually men, brothers, uncle's or father • Girls usually marry right after thier first period • Practices Endogamy by marrying within thier village, exogamy in thier culture would be marrying from another village • Settlements wouldn't be linked • Bilateral cross cousing marriage • Polygamus marriages, more specifically polygany with one man with multiple wives • The oldest wife has precedence of the other wives
Customs (Death) • Called Reahu • Lament by singing and chanting • Corpse is quickly burned, women and children absence themselves • After cremating their dead, they crush and drink thier bones in a plantain pure • A way of showing affection for the dead, intended to keep the loved ones with them forever • Helps ensure that the soul of the dead will find its way back to hedu (paradise above earth)
Customs (holiday/celebrations) • Settlements not linked by marriage or divided by war invite each other to elaborate feasts which includes gifts of valuable trade items given by the host to the guest village • Celebrate good harvest with a big feast
Cuisine • Snakes, Wild Pigs, deers, insects, larvae, fish, crabs, wild honey, nuts, shellfish, plantain, sweet potato, palm fruits, fish • 80-90% of its food is eaten from their gardens • Hunting accounts for about 10% of its food supply, as is shared equally • A Brazilian research study showed that the Yanomamo tribe has significantly low body fat and sodium, and also contain high levels of potassium, compared to other distinct populations in other continents, • Wild Honey is greatly valued
Education • Behavior is learned and taught by parents • Number system is 1, 2 and more than two • Children practice shooting and throwing, no formal school
Technology • Finished cords made from twisted inner bark. Used as materials to make hammocks • Tools are devised from materials that can be made immediately from the environment • Curare and Timbo, poison used for catching fish • Special pots used to prepare food deasts • Bow Staves; 5-6 ft longs made of palm wood very dense • Bow Staves are also made by shaving the sock with incisors • Fire Drill, a two piece gadget. The one piece of wood about 10 inches long that has several holes due to friction. The lower piece is held down by the foot while the other piece is spun until a fire ignites by feeding from the glowing dust with tinder
Citations "Hands Around the World." Native American Indian Cultures. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://indian-cultures.com/Cultures/yanomamo.html> "Pilot Guides.com:Yanomami Tribe." Pilot Guides.com:Yanomami Tribe. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://www.pilotguides.com/destination_guide/south-america/venezuela/yanomami_tribe.php>. "The Yanomami." The Yanomami. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://www.gymmuenchenstein.ch/stalder/klassen/hie/indigenous/yan.htm>. "People." ThinkQuest. Oracle Foundation. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://library.thinkquest.org/27507/people.htm>. "Yanomamo." Yanomamo. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://www1.broward.edu/~hsorkin/Lib-Arts/Projects/Fall2002/Hottinger/culture.html>. "Rainforest Facts." Rainforest Facts. Web. 05 June 2012. <http://www.rain-tree.com/facts.htm>.