Blockchain in Distribution Management (1)
0 likes | 22 Views
Blockchain technology, once synonymous solely with cryptocurrencies, has now transcended its original purpose and is making significant strides in revolutionizing various industries. In the realm of distribution management systems (DMS), blockchain technology is emerging as a game-changer, offering unparalleled transparency, security, and efficiency. This article explores the rise of blockchain technology in DMS and its profound impact on enhancing transparency and security across the supply chain.<br><br>

Blockchain in Distribution Management (1)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
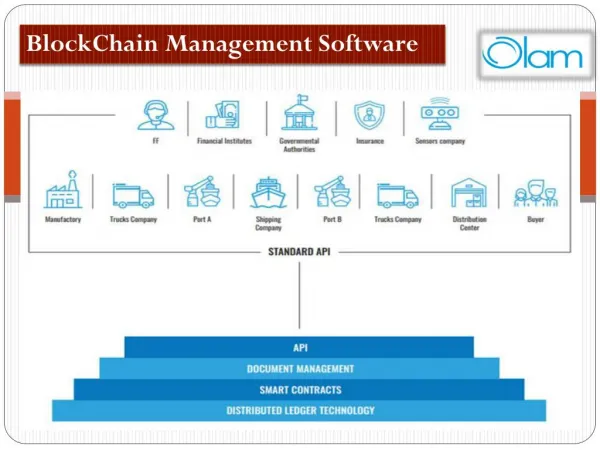
Blockchain in Distribution Management: Transparency and Security. Blockchain technology, once synonymous solely with cryptocurrencies, has now transcended its original purpose and is making significant strides in revolutionizing various industries. In the realm of distribution management systems (DMS), blockchain technology is emerging as a game-changer, offering unparalleled transparency, security, and efficiency. This article explores the rise of blockchain technology in DMS and its profound impact on enhancing transparency and security across the supply chain. Understanding Blockchain Technology At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized and immutable ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a tamper-proof manner. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and transparent record of transactions. The Role of Blockchain in Distribution Management Systems Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain enables end-to-end transparency by providing a secure and immutable record of every transaction and movement of goods across the supply chain. From raw material sourcing to manufacturing,
distribution, and delivery, stakeholders can trace the entire journey of a product with unprecedented visibility. Secure Data Management: Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of data tampering, fraud, and unauthorized access. By securely encrypting and storing data across multiple nodes, blockchain ensures data integrity and confidentiality, enhancing security throughout the distribution process. Key Benefits of Blockchain in DMS Enhanced Traceability: Blockchain enables real-time tracking and tracing of products, allowing businesses to verify the authenticity, origin, and journey of each item. This level of traceability is particularly crucial in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where product safety and compliance are paramount. Streamlined Transactions: Blockchain facilitates seamless and secure transactions between supply chain partners, eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction costs and delays. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with predefined conditions, automate contract execution, payment, and compliance, further streamlining transactions. Improved Supply Chain Efficiency : By providing a single source of truth and eliminating data silos, blockchain enhances collaboration and coordination among supply chain participants. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced errors, and faster decision-making, ultimately driving operational excellence across the supply chain. Real-World Applications of Blockchain in DMS Product Authentication: Blockchain enables product authentication through unique digital identifiers or “digital twins” assigned to each product. Customers can verify the authenticity and provenance of products by scanning QR codes or NFC tags, fostering trust and combating counterfeit goods. Track and Trace: Blockchain-powered track-and-trace solutions enable real-time monitoring of product movement, temperature, and other relevant data throughout the supply chain. This visibility helps businesses identify bottlenecks, optimize routes, and respond swiftly to disruptions, ensuring timely delivery and customer satisfaction. Challenges and Future Outlook Integration Challenges: Despite its potential, widespread adoption of blockchain technology in DMS faces challenges related to interoperability, scalability, and integration with existing systems. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration among stakeholders and investment in interoperable blockchain platforms. Future Outlook: As blockchain technology matures and standards evolve, its integration into DMS is expected to accelerate. Innovations such as tokenization, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and blockchain-based marketplaces hold promise for further enhancing transparency, efficiency, and trust in distribution management. Conclusion In conclusion, blockchain technology is poised to disrupt the traditional paradigms of distribution management by providing unprecedented transparency, security, and
efficiency. By leveraging blockchain’s decentralized ledger and smart contract capabilities, businesses can transform their distribution processes, streamline transactions, and build trust with customers and partners. As the adoption of blockchain technology continues to grow, organizations must stay abreast of emerging trends, invest in blockchain education and infrastructure, and collaborate with industry partners to unlock the full potential of blockchain in distribution management. Embrace the rise of blockchain technology in distribution management system and embark on a journey towards enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency in your supply chain operations.