Living in a River Valley Civilization: Challenges and Advancements
250 likes | 329 Views
Explore the drawbacks and solutions of living in a River Valley civilization, focusing on the Sumerian City-States along the Tigris and Euphrates. Discover how these early societies coped with lack of protection, resources, and the possibility of drought. Delve into the social hierarchy, trade, and advancements in culture, religion, and governance. Learn about the Sumerians' innovative city-building techniques and the role of women in shaping their civilization.

Living in a River Valley Civilization: Challenges and Advancements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Let’s discuss some negatives about living in a River Valley first…
Lack of protection • Easy to invade b/c no mountains or natural barriers • How did they cope? They built brick walls & moats
Lack of resources- no forests for woods, little stone and minerals • How did they cope? TRADE! • What did they trade?
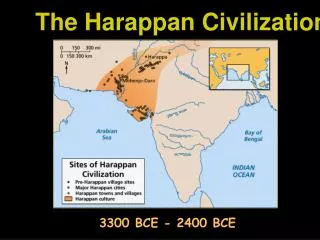
A city-what??!? • City State: a community that included a city and its surrounding lands. • Sumerian City State: • Trade • Learning • Religion • By 3,000BCE Sumer had atleast 12 city states • Famous ones were: • Babylon • Kish • Nippur • Ur
Where are they located? • Most city states are located near the mouth of the Tigris and Euphrates • The land was fertile • Farmers can grow more food • More food = bigger population
3,300 BCE - SUMER • What is a civilization? A civilization is advance form of culture that developed in cities. • For example: as we became better farmers, population increased • City leaders organized workers • Culture grew much more complex
The Sumerian City State • http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=c97e7036-9246-4258-b1f6-9586f5e1333b
The Sumerian city • Built homes out of reeds, brick and mud • Rooms around a court yard
The Ziggurat • 2220 BCE- largest most important structure in the city • It functioned as a city hall • Middle of a temple complex • This is b/c priests ran the agriculture and other things of importance
Brief Sumerian Religion • Priests = very important • Politically • Religious • Went to them for help from gods
Sumerian Social Classes • Top: kings/Priests • Upper: landowners, government officials and rich merchants • Middle: farmers & artisans • Lower: slaves
Upper class- land owners, rich merchants, government officials
Social Hierarchy • http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=3029357E-9BB7-40D5-93E2-EFFBDCA2AFFE
What was the role of Women? • Women in Sumer had more rights than they did in later Mesopotamia • Upper class women became priestesses = role of honor • Could own land • Work as merchants/weavers • Main role was still raising children