Gradients: Calculating Slopes & Elevations
80 likes | 210 Views
Learn how to calculate gradients for slopes and elevations with examples. Determine the gradient between locations or altitudes using simple formulas.

Gradients: Calculating Slopes & Elevations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
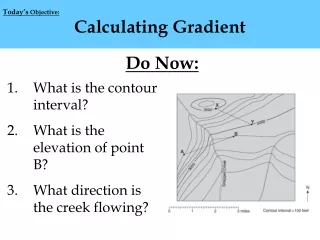
Today’s Objective: Calculating Gradient Do Now: • What is the contour interval? • What is the elevation of point B? • What direction is the creek flowing?
Gradient (or slope) • The rate of change in values between two points on a field map. • How gentle or steep the land is
Steep Gentle Steep slope – lines are closer together Gentle slope – lines are farther apart
Gradient examples - • A hiker gains 250 meters in altitude by climbing a mountain from the valley. The peak is 5 km from the valley. What is the gradient of the mountain side? 250 m G= = 50 m/km 5 km
145 m – 125 m G= 5 km = 4 m/km
Now try these . . . • Two cities are separated by 200 miles. City X has an altitude of 122 meters and City Y has an altitude of 260 meters. Calculate the altitude gradient between the two cites. 260 m – 122 m G= = 0.69 m/mi 200 mi
A map shows two locations A and B. They are 25 kilometers apart. Location A has an elevation of 535 meters and location B has an elevation of 125 meters. What is the gradient between the two locations? 535 m – 125 m G= = 16.4 m/km 25 km