Trigeminal Nerve
1.09k likes | 3.13k Views
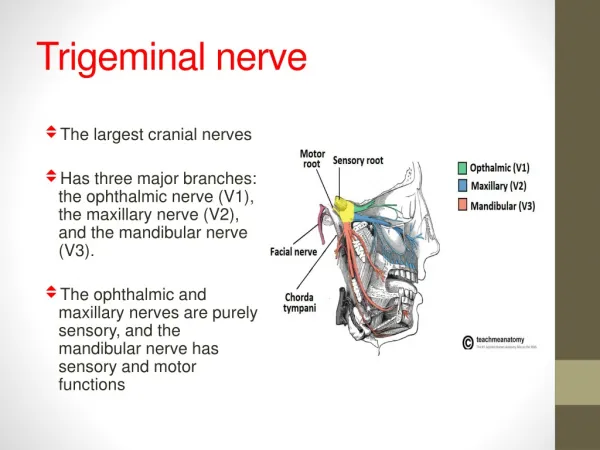
Trigeminal Nerve. Trigeminal nerve. Largest & one of most complex cranial nerves Mixed nerve Large sensory part & much smaller motor part Sensory component has 3 divisions : ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular. Motor & prinicipal sensory nuclei – midpons

Trigeminal Nerve
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Trigeminal nerve • Largest & one of most complex cranial nerves • Mixed nerve • Large sensory part & much smaller motor part • Sensory component has 3 divisions : ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular. • Motor & prinicipal sensory nuclei – midpons • Spinal tract & nucleus (pain, temp) – pons to upper cervical cord
TRIGEMINAL NERVE • Type:Mixed (sensory & motor). • Fibers: • General somatic afferent: Carrying general sensations from face. 2. Special visceral efferent: Supplying muscles developed from the 1st pharyngeal arch, (8 muscles).
TRIGEMINAL NERVE NUCLEI • Four nuclei: (3 sensory + 1 Motor). • General somatic afferent: • Mesencephalic(midbrain & pons): receives proprioceptive fibers from face. • Principal (main) sensory (pons): receives touchfibers from face. • Spinal (pons, medulla & upper 2-3 cervical segments of spinal cord): receives pain & temperature sensations from face. • Special visceral efferent: 4. Motor nucleus (pons): supplies: • Four Muscles of mastication (temporalis, masseter, medial & lateral pterygoid). • Other four muscles (Anterior belly of digastric, mylohyoid, tensor tympani & tensor palati).
TRIGEMINAL GANGLION • Site: • Occupies a depression in the middle cranial fossa. • Importance:Contains cell bodies: • Whosedendrites carry sensations from the face. • Whoseaxonsform the sensory root of trigeminal nerve.
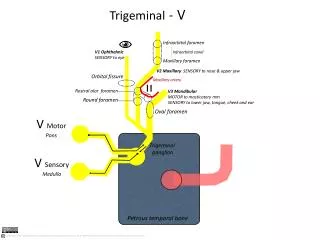
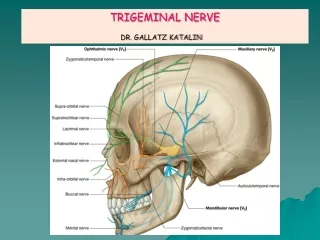
TRIGEMINAL NERVE • Emerge from middle of the ventral surface of the pons by 2 roots (large lateral sensory root & small medial motor root). • Divides into 3 divisions (dendrites of trigeminal ganglion): • Ophthalmic. • Maxillary. • Mandibular. • Axons of cells of motor nucleus join only the mandibular division.
Pure Sensory Pure Sensory C2,3 Great auricular N. Mixed Nerve Areas of Distribution of Trigeminal Nerve in the Face
OPHTHALMIC (PURE SENSORY) • Divides into:3 branches: • frontal, lacrimal & nasociliarywhich pass through superior orbital fissure to orbit. • Frontal: supplies skin of face & scalp. • Lacrimal: supplies skin of face & lacrimal gland. • Nasociliary: supplies skin of face, nasal cavity & eyeball.
MAXILLARY (PURE SENSORY) • Supplies: • Upper teeth, gums & maxillary air sinus: (posterior, middle & anterior superior alveolar nerves). 2. Face: (zygomaticofacial ,zygomatico temporal &infraorbital nerves).
MANDIBULAR (MIXED) • SENSORY BRANCHES: • Lingual: General sensations from anterior 2/3 the of tongue. 2. Inferior alveolar: Lower teeth, gums & face. 3. Buccal: Face(cheek on upper jaw) 4. Auriculotemporal: auricle, temple, parotid gland & TMJ. • MOTOR BRANCHES: to 8 muscles ( 4 muscles of mastication & other 4 muscles).
Muscles of Mastication • Masseter : close the jaw , protrude it slightly • Temporalis : close the jaw , retract it slightly • Medial pterygoids: close the jaw & protrude it • Lateral pterygoids: open the jaw & protrude it • - Unilateral pterygoid weakness – jaw deviates towards side of weak muscle
Also supplies • Mylohyoid • Ant.belly of digastric • Tensor velipalatini • Tensor tympani
Trigeminal Neuralgia • Compression, degeneration or inflammation of the 5th cranial nerve may result in a condition called trigeminal neuralgia or tic douloureux. • This condition is characterized by recurring episodes of intense stabbing , excoriating pain radiating from the angle of the jaw along a branches of the trigeminal nerve. • Usually involves maxillary & mandibular nerves, rarely in the ophthalmic division.