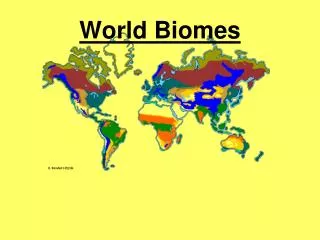
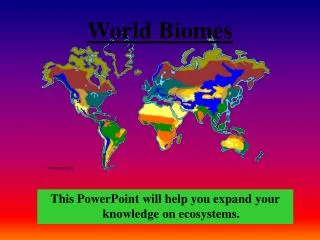
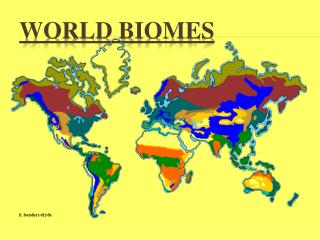
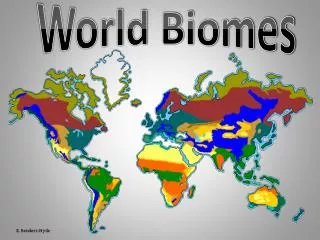
World Biomes
310 likes | 509 Views
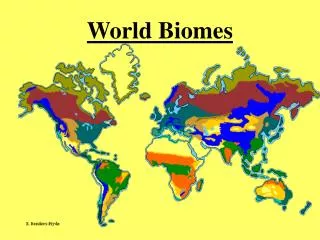
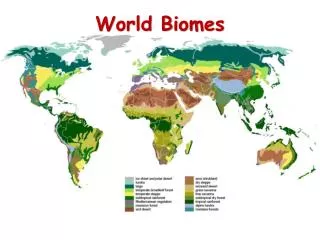
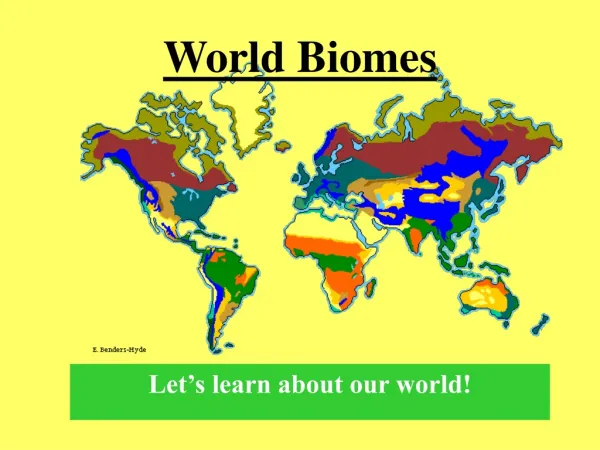
World Biomes. Rainforest. Earth's most complex land biome. Climate Region: Tropical Wet Very hot and wet Hydrologic cycle repeats often here Rains more than 90 days a year. http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysfl. Bougainvillea. Plant Adaptations

World Biomes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Rainforest Earth's most complex land biome Climate Region: Tropical Wet Very hot and wet Hydrologic cycle repeats often here Rains more than 90 days a year http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysfl
Bougainvillea Plant Adaptations • Sunlight is a major limiting factor • Little sun reaches the floor • Plants grow in layers (canopy receives most light) Bangul Bamboo
Silvery Gibbon Animal Adaptations Live in different levels of canopy Many animals are specialists and require special habitat components to survive Camouflage is common Wagler’s pit viper Slender Loris http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/rnfrst_animal_page.htm
Temperate Deciduous Forests Climate Region: Humid Continental • 4 distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, winter • mild summers and winters • Almost all are located by an ocean • Much of the human population lives in this biome http://www.runet.edu/~swoodwar/CLASSES/GEOG235/biomes/tbdf/tbdf.html
White Birch Plant Adaptations Deciduous forests grow in layers More sunlight reaches the ground compared to a rainforest so you will find more ground dwelling plants. More diversity in the deciduous forest vs. the coniferous forest due to increased sunlight. Trees adapt to varied climate by becoming dormant in winter Lady Fern Geulder Rose Birchhttp://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/deciduous_plant_page.htm
Bald Eagle Animal Adaptations • Adapt to many seasons • Lose Winter Coat • Eat from different layers of the forest Least Weasel Fat Dormouse http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/deciduous_animal_page.htm
Taigaaka Northern Coniferous Forest or Boreal Forest Climate Region: Subarctic dominated by cold, arctic air half the year, the temperature is below freezing only found in the northern hemisphere
Fireweed Balsam Fir • Low sunlight and poor soil keeps plants from growing on forest floor • Coniferous (needle-bearing) trees are abundant • Needles long, thin and waxy Plant Adaptations http://www.inchinapinch.com/hab_pgs/terres/coniferous/plants.htm
Moose • Adapt for cold winters • Burrow, hibernate, warm coat, insulation, etc. Great Grey Owl Animal Adaptations http://www.inchinapinch.com/hab_pgs/terres/coniferous/animals.htm
Savannas (Tropical Grasslands) Contain the greatest number of grazing animals on Earth. http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/savannah.html Climate Region: Tropical Wet/Dry Temperature doesn’t change much; 68◦-86◦ Dry winters and wet summers
Whistling Thorn Umbrella Thorn Acacia Plant Adaptations Grow in Tufts Resistant to Drought Many plants have thorns and sharp leaves to protect against predation. Kangaroos Paws Baobab http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/savanna_plant_page.htm
Chacma Baboon • Adapt for short rainy season—migrate as necessary • Limited food leads to vertical feeding • Reproduce during rainy season—ensures more young survive http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/savanna_animal_page.htm Zebras Animal Adaptations
Steppe Climate Region: Semiarid Less than 50 in/year precipitation Very harsh place to live Found in the middle of continents and in the lee of mountains http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/steppe.htm
Tumbleweed Sweet Vernal most abundant are plants called Bunch grasses, fine bladed grasses that grow in clumps to preserve water Plant Adaptations http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/steppe_plant_page.htm
Many migrate, hibernate or burrow during extremes in temperature and precipitation Animals Adaptations Mongolian Gerbil http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/steppe_animal_page.htm Saiga Antelope Gazelle herd
Grasslands Climate Region: Semiarid • Many different types of grasslands; some tropical and some dry • On every continent except Antarctica • Very fertile soil http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/steppe.htm
Sod-forming grasses that won’t dry out or blow away in wind. Prairie Plant Adaptations Fleabane Buffalo Grass http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/prairie_plants_page.htm
Many adaptations to survive extremes Prairie Animal Adaptations Bobcat Geoffrey’s cat Prairie dog http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/pampas_animal_page.htm
Chaparral Climate Region: Mediterranean Hot, dry summers, mild, wet winters Slight variations in seasonal temperatures…NICE! California Chaparral Mediterranean Chaparral http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/world_biomes.htm
Blue Oak Plant Adaptations Mostly low-lying shrubs and small trees. Many plants have leathery leaves to resist water loss Many plant species have oils in leaves to help them resist fire…the fire will take out “weaker” plants that don’t belong. Fairy Duster
Animal Adaptations Camouflage—to avoid predation Many animals will change their diet as the season changes. Aardwolf Puma
Deserts The driest places on Earth! Climate Region: Arid Less than 10 in/yr of rain Little to no topsoil due to high winds. Dry belt at 30º latitude http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/taiga.html
Joshua Tree Barrel Cactus Plant Adaptations: • Spines • Succulents • Thick, waxy cuticle • Shallow, broad roots Ocotollio http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/desert_plant_page.htm
Bob Cat Animal Adaptations: • Get water from food • Thick outer coat • Burrow during day • Large ears • Smaller animals = less surface area Armadillo Lizard Javelina http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/desert_animal_page.htm
Tundra One of the most fragile biomes on the planet http://www.runet.edu/~swoodwar/CLASSES/GEOG235/biomes/tundra/tundra.html Climate Region: Tundra Unusually cold and dry climate 6-10 inches of rain a year Temperature ranges from -20◦F in winter to 50◦F in summer Permafrost layer
Reindeer lichen Plant Adaptations • Growing close to the ground • Having shallow roots to absorb the limited water resources. • Trees grow less than 1 m high! Woody shrubs cottongrass
snowy owl • Small ears • Insulation, thick coat • Many visitors = migration • Little competition = Few predators Arctic fox Animal Adaptations Grizzly Bear
Alpine One of the coldest biomes on the planet Climate Region: Highland Dangerous amount of UV rays 12 in of precipitation a year Summer temperature ranges from 10◦F and 50 ◦F Night temperature almost always below freezing
Plant Adaptations • No trees can grow • Vegetation includes tussock grasses, small-leafed shrubs, and heaths
Must adapt to cold weather • Animals in the alpine biome include: mountain goats, sheep, elk, beetles, grasshoppers and butterflies. Animal Adaptations