Collective Risk Discovery Event
90 likes | 232 Views
Collective Risk Discovery Event. LESSONS LEARNED. June 18, 2013. Scenario Similarities. Collective Risk Recognition Where to go for information and assistance Capability requirements at multiple levels And across public and private spheres Impacts and Interdependencies

Collective Risk Discovery Event
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Collective Risk Discovery Event LESSONS LEARNED June 18, 2013 Confidential Information of RMTA
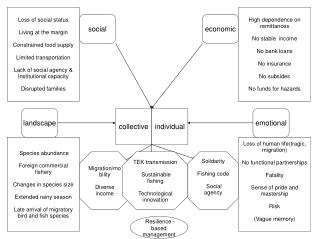
Scenario Similarities • Collective Risk Recognition • Where to go for information and assistance • Capability requirements at multiple levels • And across public and private spheres • Impacts and Interdependencies • Cyber is not just IT
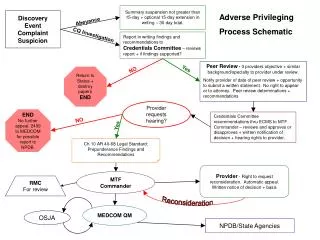
Top Level Observations • Significance of an enabling body and structure • Requirement for an enabling instrumentality • Trust among participants first, foremost, and throughout • Trust Framework is paramount; absence is a show-stopper • The Discovery Event as catalyst for Trust Framework reinforcement and improvement • To WCX: Benefits of Sharing = Preaching to Choir • Not universally true • Challenge: Spreading the Good Word more broadly
Key Findings • Category 1: Key Enablers • Category 2: Triggers to Sharing • Category 3: Barriers to Sharing
Category 1: Key Enablers • Having a formal information sharing instrumentality • Ad hoc arrangements are insufficient • Trust-building facilitation to gird Trust Framework • Trust Framework • Comply with regulatory and stakeholder interests • Public sector: State Sunshine Law considerations; private sector: proprietary and compliance concerns • Leadership Buy-in • Sharing can be counter-intuitive • Business continuity messaging • Breach costs and liability exposures
Category 2: Triggers to Sharing • Type of Attack and Scope of Attack Classifications • Collective Risk appreciation not always triggered • Data mining, DDOS, social media vs. virus infection, low level DOS • Exceeding Capacity • Network capacity • Expertise • Need for Intelligence and Situational Awareness • Nexus to Above Factors: what don’t you know? what do you need? • Key question: WHERE to go for answers? • Government role / private sector role and nexus to “collective risk”
Category 3: Barriers to Sharing • State Sunshine Laws and Regulatory Provisions • Nexus to Trust Framework to resolve many issues • Competitive, Capitalist Marketplace • Default mindset to compete and protect brand and IP • Counter-intuitive concept to share vulnerabilities • Nexus to Trust Framework • Distrust of Government • Sharing data with regulators • Sharing data with distant Federal Government • Trust is local
Core Conclusions • Community Information Sharing Hub is Essential • Convergence Point: Education, Information Sharing, Trust Building, Training, Outreach • Public-Private Partnership model • Trust is Local • Trust must be built and sustained • Trust Framework • Trust Building activities • WCX Forums are key enablers, in addition to broader WCX activities
Western Cyber Exchange Doug DePeppe doug.depeppe@i2iscorp.com 719.785.0355