Exploring Microscopes and Cell Structures
320 likes | 429 Views
Discover the world of living organisms under 1000X magnification, from cell surfaces to internal structures. Learn about different microscopes, magnification, and techniques for viewing cells. Dive into the fascinating world of biology!

Exploring Microscopes and Cell Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
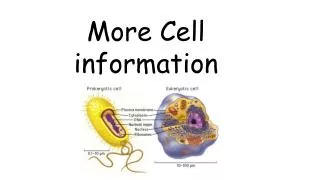
View living organisms under 1000 X? View surfaces, dead organisms 1000X -1,000,000X? View internal structures up to 1,000,000 X? LM SEM TEM Best Microscopes For?
1._____Parfocal 2. ____Clarity 3..____Field Diameter 4.____Magnification A. width of view B. stays in focus even if change objectives C. apparent increase in size D. resolving power; distinguish 2 different objects Matching:
1.__B_Parfocal 2. __D_Clarity 3..__A__Field Diameter 4.__C__Magnification A. width of view B. stays in focus even if change objectives C. apparent increase in size D. resolving power; distinguish 2 different objects Matching:
2 places to carry? Objective to first view? Where stage is to first view a slide? Arm and base Lowest (4X) Closest to objective Microscope How To’s:
Total magnification? How does the field diameter change as the magnification gets larger? Multiply eyepiece by objective magnifications. DECREASES in the same proportion (EX: if the magnification is 10X’s greater, the diameter is 10X’s smaller) How do you find?
How do you make a wet mount? • Tools? • Object on Slide • Eye dropper of water • Coverslip on top of water drop
Put metric prefixes in order:from km to Å • Kids have dropped over dead converting metrics meeting nice angels • Km hm dkm m dm cm mm µm nm Å 3 3
Convert: • 5 mm = _____µm = _____nm • 6 mm = ____________ nm • 55 nm = ___________ Å • 100 cm = ________mm = _______µm
Convert: • 5mm = 5000µm = 5,000,000nm 6 mm = ____600,000__ nm • 55 nm = ___550___Å • 100 cm = __1000__mm =__100,000__µm
What happens… • To the surface area to volume ratio when a cell gets larger? • The ratio decreases
Cell sizes • Largest? • Ostrich egg • Smallest? • mycoplasmas
PROKARYOTES Nucleoid Capsule Pili No membraned organelles EUKARYOTES Nucleus No capsule No pili Membraned organelles (like mitochondria, chloroplasts) Comparing
What 2 structures do… • Plant cells have that animal cells do not? • Chloroplasts and cell walls
What 2 structures… • Do animal cells have that plant cells do not? • Centrioles and cilia/flagella
What type of organisms have? • Ribosomes? • All (prokaryotic, plant and animal) • Plasma membranes? • All (prokaryotic, plant and animal)
DNA • Where would you find it in a cell? • In nucleus • How is chromatin related to DNA? • Chromatin is DNA + protein
ER • How is Rough ER different from Smooth ER? • In structure? • Rough ER has ribosomes embedded in it, smooth ER does not • In function? • Rough ER carries materials to ribosomes to assemble amino acids into proteins, smooth ER makes lipids
How do vacuoles differ? • In plants? • Large central vacuole • In animals? • Smaller (usually lysosomes around them)
Put in order from largest to smallest in an animal cell: • Mitochondrion ribosomes nucleus lysosome vesicle • Nucleus • Mitochondrion • Lysosome • Vesicle • ribosome
How are cilia and flagella different? • Length? • Cilia are shorter and flagella are longer • Number? • Cilia are very numerous and flagella usually only one or a few
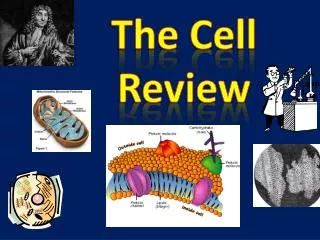
Golgi Apparatus Attached or not connected? Repackage proteins or carry materials? ER Attached or not connected? Repackage proteins or carry materials? How are they different?
Golgi Apparatus not connected Repackage proteins ER Attached carry materials How are they different?
In animal or plant cell? • Mitochondrion? • In Both animal and plant cells • Chloroplasts? • Only in plant cells
In animal or plant cell? • Mitochondrion? • In Both animal and plant cells • Chloroplasts? • Only in plant cells
Chloroplast or Mitochondrion? • Wavy membrane interior? • Mitochondrion • Green • Chloroplast • Site of photosynthesis • Chloroplast • Powerhouse • mitochondrion
Trace the path of protein. Which happens first, second…? • A. Vesicles carry protein to Golgi. • B. Proteins are assembled in ER • C. Proteins are stored in the cell • D. Golgi repackages the proteins • ANSWER: B, A, D, C • See diagram on the next slide
Cytoskeleton • What are the three types of cytoskeleton? • Microtubules microfilaments centrioles • What is the purpose of centrioles? • Cell division • What are some jobs of microtubules? • Support, movement
Which cell covering? • Is around all types of cells (prokaryotes and eukaryotes)? • Plasma membrane • Is around only plant and prokaryotes cells? • Cell wall • What covering is also outside the prokaryotic cell? • Capsule
Cell Theory • What scientist made the first microscope? • Leewenhoek • Who first coined the word “cells?” • Hooke
Cell Theory • Fill in the blanks: • All cells come from: • Pre-existing cells • The basic unit of life is a: • Cell