Supply and Demand
170 likes | 355 Views
Supply and Demand. Produced by J.R. Table of Contents. Overview of Supply and Demand Demand, its definitions and subspecies Supply, what it is and yada yada… Subsidies. So What Is S and D?. A simple economic model based on the idea that people act out of their own self-interest

Supply and Demand
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Supply and Demand Produced by J.R.
Table of Contents • Overview of Supply and Demand • Demand, its definitions and subspecies • Supply, what it is and yada yada… • Subsidies
So What Is S and D? • A simple economic model based on the idea that people act out of their own self-interest • First introduced by Alfred Marshall in Principles of Economics, published in 1890 • Not written of by the brilliant economists Smith, Mills or Malthius
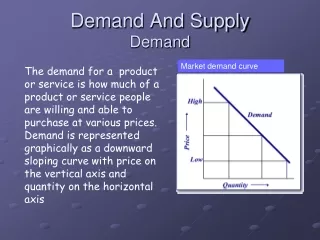
What is Demand? The amount of good that people (or consumers) are willing and/or able to buy (or consume)
What is Utility? Utility = How much satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming, using or abusing a good or service Utility declines the more there is of something
What Influences Demand? • The price of the good • The consumer’s income • If people want/like the goods • Fashion • Amount of substitutes (copies of good) • Demand for goods used at the same time • The “Sheep” effect, celebrities, friends etc are wearing/buying/using etc the good
What Makes A Demand Curve Change? • Price never shifts a demand curve • A fall in quantity, as in Q1 – Q2 can be called a “contraction in demand.”
Where a Curve can Shift • A demand curve can shift if there is a change in its customers. • If there is a change in income, taste, fashion or etc then… • The Curve Shifts
What is Supply? The amount of a good that vendors are willing and/or able to sell at any given price
What Influences Supply? • The price of the good • The amount of “competitive goods” or look-alike products • The cost of making the good • The amount being produced • Unforeseen events (earthquakes, strikes, another gold rush…)
Looking at Supply Curves • Changes in price never shift the supply curve • Increase in quantity from Q1-Q2 is called an expansion in supply
Supply Curves Shift Only… If there is: • A change in costs • A change in the number of goods • An unforeseen event (earthquake…) Increase in supply shifts curve to right
The Area in-between the two curves around where the P and Q lines collide is the equilibrium. • If the price is too high (well above equilibrium) then there is excess supply • If the price is too low (well below equilibrium) then there is excess demand • Excess supply drives prices down, excess demand drives prices up
Subsidies • A subsidy, free money given by the government to an industry, makes the industry want to produce more of a good. Thus pushing down the supply curve. • Prices falls by less than subsidy, industry keeps money
Conclusion • Supply and Demand is a simple economic model that just makes sense when looking at human nature • The goods that there are the least of are usually the most valuable • Once there becomes a lot of something then the price usually moves down • Don’t sweat it, just think baseball cards
If you want the exact link to learn more, or review go to: http://www.bized.ac.uk/stafsup/options/notes/econ207.htm#Heading80