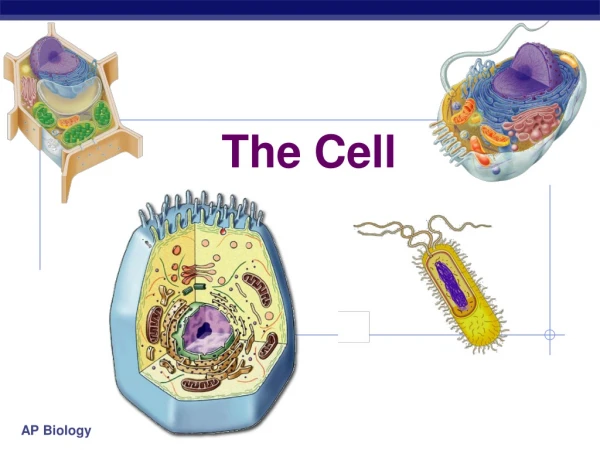
The Cell
280 likes | 482 Views
The Cell. Introduction. The cell is defined as the smallest unit that can carry on all the processes of life There are unicellular organisms which are one celled like a paramecium Multicellular organisms contain more than one cell. Cell Theory.

The Cell
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction • The cell is defined as the smallest unit that can carry on all the processes of life • There are unicellular organisms which are one celled like a paramecium • Multicellular organisms contain more than one cell
Cell Theory • All living things are composed of one or more cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things • New cells only come from existing cells
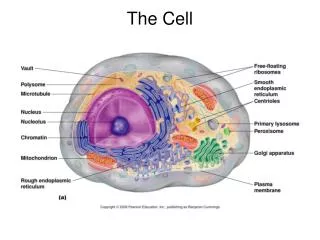
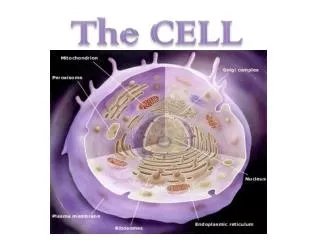
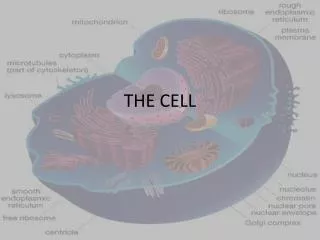
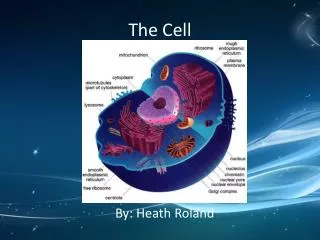
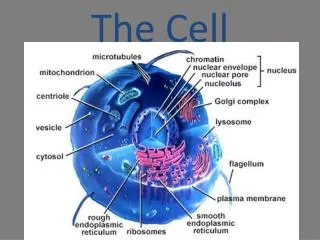
Internal Structure and Organization • Cells differ in their internal organization • The nucleus directs the activity of the cell and contains the DNA • In addition to the nucleus, there are smaller structures called organelles • An organelle is a cell component (part) that performs a specific function in the cell (a little organ) • Cells that contain both a nucleus and organelles are called eukaryotes (yoo-KAR-ee-OTES) • Plants, animals, fungi, & protists • Cells that lack a nuclei and organelles are called prokaryotes (pro-KAR-ee-OTES) • Bacteria are prokaryotes
Parts of the Cell • Although there is not a typical eukaryotic cell, most cells have 3 basic parts • Cell Membrane/Wall • Cytoplasm • Nucleus
Parts of the Cell (cont) • Cell Membrane • Separates cell from external environment, gives shape and flexibility • Barrier that keeps some molecules out but allows some in (called a semipermeable membrane or selectively permeable membrane) • Ribosomes • Most numerous • Make protein • Spherical structure
Parts of a Cell (cont) 1. Cell membrane 1 The red dots on the pink are the ribosomes
Parts of the Cell (cont) • Cytoplasm • Jellylike material found inside the cell (the area outside of the nucleus) & contains water, salts and organelles • Cytoskeleton • Made of microfilaments and microtubules • Helps the cell maintain shape and movement (amoebas to crawl)
Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm
Parts of the Cell (cont) • Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R. for short) • Membrane system of folded sacs and tunnels • Smooth E.R. has few or no ribosomes on it • Function as intercellular highways • Also function as a storage area for proteins • Rough E.R. contains lots of ribosomes and produces lots of protein • Golgi Apparatus • Processing, sort, and package proteins and other materials from the E.R. for storage in the cell or secretion outside the cell • Consists of a stack of membranes or sacs filled with fluids
1. Rough ER 1 2 2. Smooth ER 3. Golgi Apparatus 3
ReviewThumbs Up-7 Up • T F A cell is defined as the smallest unit that can carry out at least 1 process of life. • T F The movie Jurassic Park illustrates 1 segment of the Cell Theory. • T F Organelles have specific functions. • T F The 3 common parts of a eukaryotic cell are the cell wall, nucleus & chloroplast. • T F The cell membrane separates the cell from the external environment. • T F Ribosomes are found on the smooth ER. • T F Cytoplasm is found inside the nucleus.
Parts of the Cell (cont) • Mitochondria • Respiration centers of the cell • Convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use • ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is formed here which provides the chemical reactions in the cell • Lysosmes • Contain digestive enzymes • Small spherical shaped • Found primarily in animal and fungal cells • They digest food particles, disease-causing bacteria captured by white blood cells and worn out cells and cell parts
Parts of a Cell (cont) • Vacuoles • Saclike structure • Store materials like water, salts, proteins, and carbs • In many plant cells there is a large central vacuole filled with fluid • Also found in some unicellular organisms & some animals
1 1. Vacuole
1. Mitochondria-powerhouse of the cell 2 1 2. Lysosmes-G-men of the cell
Parts of the Cell (cont) • Cilia and Flagella • Extend from the surface of the cell • Function in movement • Cell Nucleus • Nucleic acids are synthesized here & directs cell activity • The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and has pores that allow material to move in and out of the nucleus • The nucleus contains a small, dense region known as the nucleolus which begins the assembly of ribosomes
Cilia Flagella Allows cell to move
1. Chromatin-DNA that condenses to form chromosomes 3 2 1 2. Nucleolus-begins the assembly of ribosomes 3.Nuclear envelope-allows materials to move in and out of the nucleus 4 4. ER-intercellular highway Nucleus
Review • T F The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell. • T F Lysosmes can be compared to garbage men. • T F Cilia and flagella are internal structures that help with cell movement. • T F The nucleus directs cell activity. • T F The nuclear envelope ensures that nothing gets in or out of the nucleus. • T F Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus.
Cell Parts (cont) • Chromatin • Spread throughout the nucleus • DNA bound to protein • During cell division it condenses to form chromosomes • Chromosomes • Threadlike structures that contain genetic information • Centrioles • Found only in animal cells • Located near the nucleus • Organizes cell division
1. Centrioles 1 Chromosome
Plant Cells • Differences between plant and animal cells • A cell wall surrounds the cell membrane which helps support & protect the cell • Plastids store food or pigments • Cell Wall • Rigid and made of cellulose • The cellulose is difficult for man and other animals to digest
Plant cells (cont) • Plastids • Depend on light as a source of energy • Plastids convert solar energy to chemical energy • Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight • Chromoplasts synthesize & store pigments which trap light and give plants color • Leucoplasts store food such as starches, proteins, and Lipids
1 1. Chloroplasts-contain chlorophyll
Review • T F Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. • T F Chromosomes are only found in animal cells. • Centrioles are found only in plant cells and organize cell division. • T F The cell wall is made of cellulose. • Cellulose is high in fiber, that is why fruits and veggies make a good diet food. • T F Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. • T F Another name for lipids is fats.