Stem Cells
90 likes | 375 Views
Stem Cells. Differentiation. The process by which cells specialize into different types of cells Some cells become heart cells, brain cells, liver cells, skin cells, etc.. There are about 260 different cell types in the body!. Stem Cells.

Stem Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Differentiation • The process by which cells specialize into different types of cells • Some cells become heart cells, brain cells, liver cells, skin cells, etc.. • There are about 260 different cell types in the body!
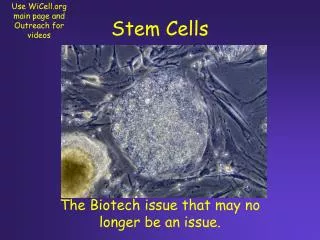
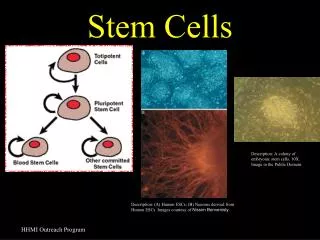
Stem Cells Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the remarkable ability to develop into different types of cells into the body They serve as sort of a repair system for the body, they can theoretically divide without limit to replenish other cells while the person or animal is still alive When a stem cell divides, each stem cell has the potential to remain a stem cell, or become another type of cell
Types of Stem Cells Embryonic stem cells Adult stem cells Multipotent, which means these cells are partially differentiated, but can form a limited number of tissues Taken from fetal tissue, umbilical cord blood, and adult stem cells Used in research to hopefully treat diseases one day • Pluripotent cells which mean they can form any of the 260 cell types • Easier to work with than adult stem cells • Taken from the interior of a blastocyst (5-14 day old embryo) • Being used in research to hopefully treat certain diseases one day • Ethical debate over whether or not to use these stem cells
Embryonic stem cells are removed from the inner layer of a blastocyst-then transferred into a Petri dish with nutrient medium to grow cells
Stem cells being removed from inner layer of a blastocyst mass- neat!
How can stem cells be used to treat/cure diseases? • Stem cells can be used to grow healthy cells and tissues and used in medical therapies to replace diseased tissues in sick people • Diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, Alzheimers disease, spinal cord injuries, burns, heart disease, stroke, and many more offer hope with stem cell research
Ethical Concerns of Embryonic Stem Cell Research(ESTR) • Some people view the destruction of embryos as murder, and thus, do not support ESTR, only adult stem cell research • Others think the life of people suffering with diseases is more important than embryos not yet fully developed into a human being, so these people support ESTR • What do you think? Write me a half page to one page essay on your opinion on embryonic stem cell research (yes, this is your homework- due Thursday)