Cell Division
290 likes | 426 Views
Cell Division. http:// www.youtube.com / watch?v =VlN7K1-9QB0. Why must cells divide?. Allow for efficient transport Growth, development, and repair of multicellular organisms Reproduction of unicellular organisms. Binary Fission. http:// www.youtube.com / watch?v = gEwzDydciWc.

Cell Division
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Why must cells divide? • Allow for efficient transport • Growth, development, and repair of multicellular organisms • Reproduction of unicellular organisms
Binary Fission • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gEwzDydciWc
What 2 processes maintain homeostasis in terms of cell number? • Division • Apoptosis (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6KVQzYO_2tY)
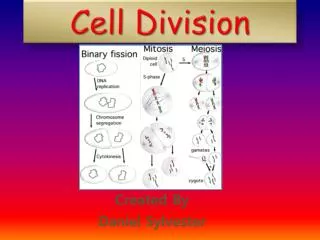
Interphase • DNA in chromatin form • Nuclear envelope in tact • Inactive centriole • Carrying out normal function
Prophase • Nuclear envelope breaks down • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes • Centrioles move to poles and begin making spindle fibers (aster)
Metaphase • Chromosomes line up at “metaphase plate” • Spindle fibers attach to centromere of chromosome
Anaphase • Spindle fiber shorten and pull apart the sister chromatids • Sister chromatids move to opposite poles of cell becoming daughter chromosomes
Telophase • Chromosomes decondense to chromatin • Nuclear envelope reforms • Spindle fibers break down • Cytokinesis begins
End Product • 2 daughter cells with identical chromosome number
Division in Prokaryotes • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gEwzDydciWc&feature=related