Photosynthesis
240 likes | 255 Views
Photosynthesis. Chapter 8. Photosynthesis -. How do Plants make oxygen and food?. Autotrophs and heterotrophs. All cells need energy to survive. All plants, some bacteria, and some protists are able to use light energy from the sun to produce food energy .

Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis Chapter 8
Photosynthesis - How do Plants make oxygen and food?
Autotrophs and heterotrophs • All cells need energy to survive. All plants, some bacteria, and some protists are able to use light energy from the sun to produce food energy. - autotroph (producer): organisms that use the sun to make their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis - heterotroph (consumer): organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat other organisms for food
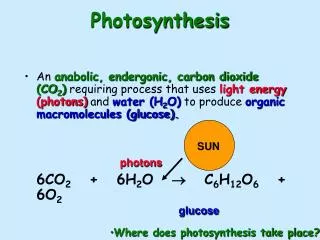
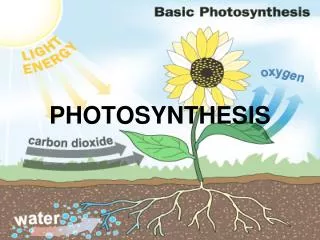
Photosynthesis vs. chemosynthesis • photosynthesis: process to turn light into carbs; carbon dioxide and water go in, carbohydrates and oxygen come out; basis of all food chains and the carbon cycle • chemosynthesis: a similar process that uses heat/chemicals (like in a volcano) instead of sunlight to make carbohydrates. Very rare! Found in some bacteria that live in underwater hot vents.
The Photosynthesis Equation reactants products • MEMORIZE THIS!
Trapping Sunlight • Plants contain pigments, which are light absorbing molecules that trap energy from the sun. • The main pigment is chlorophyll, which traps all light except GREEN light. The Green is reflected, which gives plants their green color. • Accessory pigments (orange, yellow, red, and blue) help trap other colors of light, including some of the green.
Light and Pigments • Chlorophyll is not the only pigment • Carotenoids: plants also contain red, yellow, and orange pigments that absorb other wavelengths of light. We see these pigments in fall leaves
Leaf Structure • A – cross section of the leaf • B – spongy middle layer used for photosynthesis, but filled with air spaces • C – air space • D – Waxy cuticle to keep water inside the leaf • E & H – epidermis cells that make the cuticle • F – palisade layer near the top where most photosynthesis occurs • G – transport veins that consist of xylem (for water) and phloem (for food) • I – guard cells open and shut the stomata (holes) in the leaf for gas exchange; close stomata when it’s too hot to prevent transpiration (water loss) • J - stomata
Chloroplast Structure • photosynthesis takes place inside a chloroplast
Inside a Chloroplast • The “stacks of coins” inside chloroplasts are actually thylakoids, sac-like photosynthetic membranes that contain pigments to capture sunlight • thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana(singular: granum) • the gel that surrounds the grana is called the stroma
Two Reactions of Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis is divided into two stages: 1. light-dependent reactions: Traps the sunlight using a series of proteins and pigments called an electron transport chain. Also splits a water molecule during this time and releases oxygen. Captures energy for Calvin Cycle. 2. Calvin Cycle: uses trapped energy to make sugar; SIX molecules of CO2 make ONE six-carbon sugar (C6H12O6)
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis is run by enzymes, so environment matters • water: too little water will slow or stop photosynthesis • temperature: optimum (best) temperature is between 0C and 35C where water is liquid • light: more light, more photosynthesis • Light color: white light is best; green light is worst
Question 1 • Which of the following are autotrophs? a. impalas b. plants c. leopards d. mushrooms
Question 2 • One of the principal compounds that living things use to store energy isa. DNA b. ATPc. H2Od. CO2
Question 3 • In addition to light and chlorophyll, photosynthesis requires a. water and oxygenb. water and sugarsc. oxygen and carbon dioxided. water and carbon dioxide
Question 4 • The leaves of a plant appear green because chlorophyll a. reflects blue lightb. absorbs blue lightc. does not absorb green lightd. absorbs green light
Question 5 • The products of photosynthesis are a. sugars and oxygenb. sugars and carbon dioxidec. water and carbon dioxided. hydrogen and oxygen
Question 6 • Which organelle contains chlorophyll? a. b. c. d.
Question 7 • The first process in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is a. light absorptionb. electron transportc. oxygen productiond. ATP formation
Question 8 • Which substance from the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is a source of energy for the Calvin cycle?a. ADP b. ATP c. H2O d. pyruvic acid
Question 9 • The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis are also known as the a. Calvin cycleb. Priestley cyclec. Ingenhousz cycled. van Helmont cycle
Question 10 • Which equation best summarizes the process of photosynthesis? a. b. c. d.