Glaciers
300 likes | 438 Views
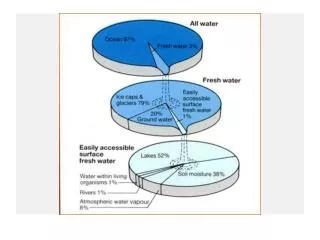
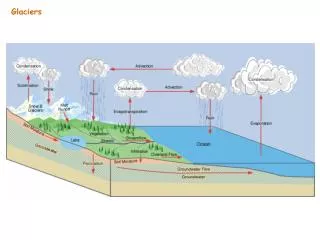
Glaciers. What is a glacier?. Glacier- A large moving mass of snow and ice. Where are glaciers found?. How are glaciers formed?. Snow falls on the side of a mountain and begins to collect. As more and more snow piles up, it creates pressure

Glaciers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a glacier? • Glacier- A large moving mass of snow and ice
How are glaciers formed? • Snow falls on the side of a mountain and begins to collect
As more and more snow piles up, it creates pressure • The snow is packed down into ice and accumulates as a large sheet of ice
Snow into Ice • Snow becomes packed • As its packed, it turns to ice
Pressure and Gravity • As more snow falls, glaciers become thicker and heavier • Gravity pulls glaciers downward with great pressure against the ground
Movement • Glaciers move very slowly • Glaciers slide, or creep over the ground
Calving Calving occurs when pieces of a tidewater glacier break off and fall into the sea
Crevasses • As Glaciers move, the ice on top bends and cracks • These cracks are called Crevasses
Glacier Snout • Front end of a glacier. Also called the terminus.
Erosion • As Glaciers move, they pick up debris • Stones and boulders are picked up and carried along • Using these stones and their weight, glaciers grind and carve the landscape
Erosion • A glaciated valley in the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest showing the characteristic U-shape and flat bottom.
Erosion • The Llanberis Pass in Snowdonia National Park, north Wales, is typical of a U-shaped valley formed by glacial erosion.
Icebergs Most of the icebergs are found under water, making them very dangerous to ships.
Glacier Fun • When glaciers melt they deposit materials, creating terminal moraines • Let’s see if we can use a model to show what this looks like. • Read C10 on Terminal Moraines
Picture References • http://www.instablogsimages.com/images/2007/09/26/glacier_6914.jpg • http://omega.utu.fi/images/hintereisferner_aerialview.jpg • http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/images/lithosphere/glacial/glacier_zones.jpg • http://www.thegreenhead.com/imgs/sno-baller-snow-ball-maker-7.jpg • http://www.rosssea.info/pix/big/Commonwealth-Glacier-Stream.jpg • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Grosser_Aletschgletscher_3178.JPG • http://www.scienceclarified.com/images/uesc_05_img0282.jpg • http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.dkimages.com/discover/previews/793/10042113.JPG&imgrefurl=http://www.dkimages.com/discover/DKIMAGES/Discover/Home/Science/Earth-Sciences/Geology/Landform-Evolution/Glaciers-and-Ice-Sheets/Features/Features-6.html&usg=__0OxwO-5rZGMLp8b-t8R7NM2pfwg=&h=909&w=1136&sz=362&hl=en&start=1&sig2=uw2VFJeSEzViDxRebtnd3A&um=1&tbnid=PdZUweB8OcexvM:&tbnh=120&tbnw=150&ei=JU8nSdDdBY628AS1jN3_Ag&prev=/images%3Fq%3Ddiagram%2Bof%2Ba%2Bglacier%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26rlz%3D1T4DKUS_enUS252US253%26sa%3DN • http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/sharemed/targets/images/pho/t628/T628797A.jpg
Picture References • http://i212.photobucket.com/albums/cc267/aaronbenor/IMG_1577.jpg • http://image24.webshots.com/24/7/7/77/30070777GXwKXzPTlI_fs.jpg • http://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/graphic0/geomorph/longsect.gif • http://gsc.nrcan.gc.ca/landscapes/photos/photographs/yukon/otherareas/img3_03_02.jpg • http://go.owu.edu/~jbkrygie/krygier_html/geog_111/geog_111_lo/geog_111_lo14_gr/kellysgrooves2.jpg • http://lh6.ggpht.com/_XxTGi_YtwxM/R_YnKaxefzI/AAAAAAAAAOI/8VrIFEVziyw/_98.JPG • http://www.geology.um.maine.edu/user/Leigh_Stearns/teaching/kelley_island.jpg • http://www.tiscali.co.uk/reference/encyclopaedia/hutchinson/m0035305.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Stillaguamish_River_18434.JPG • http://uk.encarta.msn.com/media_461518239_761574629_-1_1/Hubbard_Glacier.html • http://www.geographyhigh.connectfree.co.uk/s3glacgeoghighuplandform2.html
Picture References • http://www.aoqz76.dsl.pipex.com/Web%20Page%20Components/Wallpaper/Landscapes/Iceberg.jpg • http://www.pathwaymedicine.com/images/ICEBERG%20web.jpg • http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.wunderground.com/data/wximagenew/a/anghy85/465.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.wunderground.com/blog/mitzy259/comment.html%3Fentrynum%3D1%26tstamp%3D200607&usg=__lnlvCzs83BsZlOsYEUlYGvU95IY=&h=449&w=640&sz=152&hl=en&start=4&sig2=0g7VCNl-ZFNPQbL-aVRMMQ&um=1&tbnid=iWIduoGdOWAtJM:&tbnh=96&tbnw=137&ei=Rk0nSeysPIOs8ASo5riBAw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dparts%2Bof%2Ba%2Bglacier%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26rlz%3D1T4DKUS_enUS252US253%26sa%3DN • http://www.swisseduc.ch/glaciers/glossary/terminal-moraine-en.html