Essential Networking Terminology
130 likes | 136 Views
There are various terms that are frequently used in networking and it is essential to have knowledge about these terms.<br>

Essential Networking Terminology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
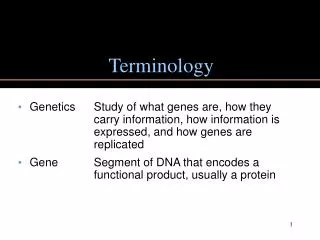
Table of Contents • Connection, Packet, Network Interface • LAN, WAN • Protocol • Port, Firewall • NAT, VPN • TCP/IP Model • Interfaces • Medium Access Control • IP, ICMP, TCP
Connection, Packet, Network Interface • Connection- In the context of networking, a connection indicates those pieces of related information which a network transfers. Prior to the transfer of data, a connection is built which exists till data transfer takes place. • Packet- A packet carries data between two ends. It refers to the most basic unit of data that a network transfers. Each packet has a header portion. Information about the packet, such as source, destination, timestamps etc. is contained in this portion. The data that is being transferred is contained in the main portion, which is usually called the body. • Network Interface- It refers to any type of software interface or networking hardware. It can be associated with a physical device or it can be a virtual interface’s representation.
LAN, WAN • LAN- LAN is the abbreviation for Local Area Network. It is either a network or a certain portion of a network which cannot be accessed publicly by the Internet. Its examples are the networks in houses and offices. • WAN- WAN is the abbreviation for Wide Area Network, which in terms of a network is more extensive than a LAN. It usually refers to the Internet. Any interface that is connected to a WAN is assumed to be reachable through the Internet.
Protocol • A protocol refers to a collection of standards and rules which specifies the language that a device uses for communication. There are various protocols which are used in networking. These are usually implemented in different layers. Its examples are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), UDP (User Datagram Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) etc.
Port, Firewall • Port- A port is essentially an address that is associated with a single machine which can be linked to a specific piece of software. It does not indicate a physical interface or location. It enables a server to use more than one application for the purpose of communication. • Firewall- A firewall refers to a program that functions by creating rules for different types of traffics’ acceptability on the relevant ports. It decides whether the incoming as well outgoing traffic to a server should be allowed or not. Usually a firewall blocks those ports that are not being used by a particular application on a server.
NAT, VPN • NAT- NAT is the abbreviation for Network Address Translation. It refers to the way that is involved in translating incoming requests to a routing server. Usually physical LANs implement it for routing requests via an IP address to the relevant backend servers. To digress, servers are used by web hosting companies for storing the data of websites and making websites accessible. The most reliable web hosting companies are usually described as the “Best Cloud Hosting Company”, the “Best Linux Shared Web Hosting Company”, the “Best Windows Shared Hosting Company” etc. • VPN- VPN is the abbreviation for Virtual Private Network. It connects separate LANs over the Internet, while ensuring privacy. It is used for connecting remote systems, usually for security related reasons.
TCP/IP Model • The TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)/IP (Internet Protocol) model, which is known as the Internet Protocol suite refers to a layering model. It is not only simple but is widely used. This model has 4 layers and follows a horizontal approach. Session and presentation layers are used in the application layer in TCP/IP. This type of model network layer provides connectionless services. It is not easy to replace protocols in TCP/IP model.
1-800-123 -8156 Whoa! That’s a big number, aren’t you proud?
Interfaces • Interfaces refer to the points that are associated with networking communication. Each interface has a virtual or a physical networking device. Usually a server has one configurable network interface for every wireless Internet card or Ethernet that is being used. Additionally, it specifies a virtual network interface, which is known as the localhost interface. This serves the purpose of connecting processes and applications on a computer to other processes and applications. Often one interface is configured by administrators to service traffic to the Internet and some other interface is configured for a private network or LAN.
Medium Access Control • Medium Access Control is a communications protocol which is used for differentiating specific devices. Every device should have a unique Media Access Control Address (MAC Address) which differentiates it from the other devices on the Internet. When devices are addressed using their MAC address, it lets a device be referenced uniquely, regardless of its name being changed by any software during operation.
IP, ICMP, TCP • IP- IP is the abbreviation for Internet Protocol and is one of the main protocols that ensures the functioning of the Internet. Its implementation takes place in the Internet layer of the IP/TCP model. • ICMP- ICMP is the abbreviation for Internet Control Message Protocol and is used for exchanging messages among devices for indicating availability or error related conditions. ICMP packets are used in various network diagnostic tools and serve as a feedback mechanism with regard to network communications. • TCP- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is implemented in the transport layer of an IP/TCP model for establishing reliable connections.
Thanks! ANY QUESTIONS? www.htshosting.org