Fundamental niche
430 likes | 821 Views
Realized niche. Fundamental niche. Character displacement in beak size in poulations of Galapagos finches. # prey predator kills; on predator efficiency = c, # prey, # predators. Efficiency of converting kills to new predators. Death rate of predators in absence of prey. # kills.

Fundamental niche
E N D
Presentation Transcript
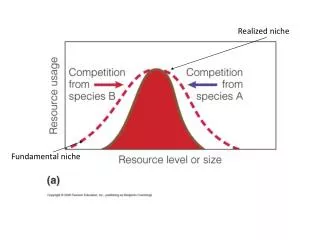
Realized niche Fundamental niche
Character displacement in beak size in poulations of Galapagos finches
# prey predator kills; on predator efficiency = c, # prey, # predators
Efficiency of converting kills to new predators Death rate of predators in absence of prey # kills
Type I functional response Daphnia magna consuming yeast cells
Type II Functional response Parasitoid that attacks cocoons of pine sawfly
Cryptic coloration in the flounder, which is capable of changing their color and pattern rapidly to match bottom sediments.
Cryptic coloration the walking stick, which feeds on leaves.
Aposematism: Monarch Batesian mimicry: Viceroy Müllerian mimicry
Effects of grazing by beetle (Gastrophysa viridula) on dock plant (Rumex crispus)
Interaction between herbivory and pollution • N pollutants: decrease C:N ratio >> more palatable • Combined stress of herbivory and pollution may be synergistic
Symbiosis • Close association between individuals of two or more species • Includes parasitism and mutualism • Parasitism: member of one species (parasite) feeds on, but usually doesn’t kill member of another species (host) • Mutualism: an interaction between individuals of two or more species in which the growth, growth rate, and/or population size are increased in reciprocal association
960 g alfalfa Methane, CO2 Volatile fatty acids: 57 g Microbial cells: 128 g Minerals: 43 g Rumen dry matter: 343 g • 4.7 L total volume • 20% volume = • microorganisms 369 g feces (50 g bacteria; 319 g food residue
Cleaner-customer mutualism Indicator indicator:honeyguide Mutualism b/t bird and honey badger or humans
Deep Sea Pompeii Worm Alvinella pompejana Close-up showing the bacteria-coated filaments that cover the body of this hydrothermal vent worm. � 2004 Peter Batson/Image Quest Marin
protoeukaryote Krebs cycle- containing bacterium promitochondrion spirochaete eukaryote cyanobacteria mitochondria flagellate chloroplasts
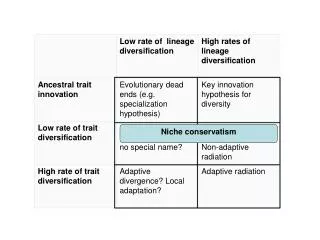
Lokta-Volterra Mutualism??