Nervous System
160 likes | 401 Views
Nervous System. Organization of the Nervous System Nervous Tissue: Structure & Function. Nervous System. Organization of the Nervous System Nervous Tissue: Structure & Function. The Nervous System. The master controlling & communicating system of the body

Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nervous System Organization of the Nervous System Nervous Tissue: Structure & Function
Nervous System Organization of the Nervous System Nervous Tissue: Structure & Function
The Nervous System • The mastercontrolling & communicatingsystem of the body • It uses electrical impulses and chemical transmission, • which are rapid and specific to cause an almost immediate response Sensory input Motor output
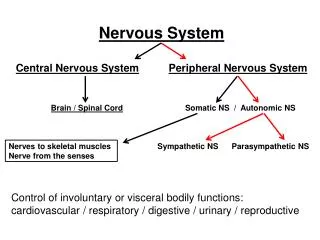
Organization of the nervous system Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) Peripheral Nervous System (cranial and spinal nerves) Sensory (afferent) Motor (efferent) Sense organs Somatic (voluntary) Skeletal muscles Autonomic (involuntary) Cardiac and smooth muscle, glands Parasympathetic Sympathetic
CNS vs. PNS Environmental cue/sensory Central nervous system Protective response
Structure & Function • There are two (2) types of cells that make up the nervous tissue: • supporting cells • neurons Supporting Cells: Oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Astrocyte Microglial cell
Structure & Function Supporting Cells: • Astrocytes: star-shaped cells with swollen ends, most abundant • anchor to neurons & connect them to blood capillaries. • Microglial cells: spider-shaped phagocytes that dispose of debris, • including dead brain cells and bacteria. • Ependymal cells: cells that line the cavities of the brain & spinal cord. • The beating of the cilia helps circulate cerebrospinal • fluid that form a protective cushion around the CNS. • Oligodendrocytes: cells that wrap around neurons forming the myelin • sheaths
Structure & Function Neurons: Mitochondria Node of Ranvier Nucleus Cell body Dendrite One Schwann cell Axon Axon terminal myelin sheath
Neural Directional Signal Neurons: Axon Hillock
Neural Terminology • Nuclei – clusters of neural cell bodies found in CNS • Ganglia – clusters of neural cell bodies found in PNS • Tracts – bundles of nerve fibres running through CNS • Nerves – bundles of nerve fibres running through PNS • In Central Nervous System: • White matter – dense collections of myelinatedfibers (tracts) • Grey matter – dense collections of unmyelinatedfibers & cell bodies
Neural Transmission Electrical Impulse Chemical Transmission at neural synapse
Reflexes • Rapid, predictable and involuntary responses to stimuli • Similar to one-way street – it always goes in the same direction • The neural pathways that reflexes transmit through is called: • reflex arcs(involve both CNS and PNS structures)
Central Nervous System The Brain:
Functions of the Brain 1. Cognitive Thinking 2. Voluntary eye movement 3. Motor & Speech production 4. Motor skills development 5. Sensation 6. Language comprehension 7. Vision 8. Auditory 9. Memory 10. Muscle coordination
Sleeping Pattern of the Brain Electroencephalography (EEG) is used to obtain a record of brain wave. Electrodes are positioned on the patient’s scalp i) Alpha = awake, relaxed; ii) Beta = awake, alert; iii) Theta = drowsy, dreaming; iv) Delta = deep sleep