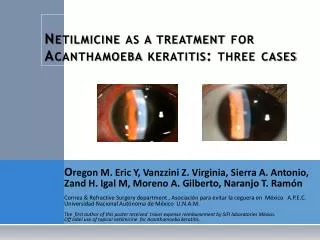
Acanthamoeba keratitis case
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Case presentation Mohammad Abdullah Bawtag Case presentation Resident of Ophthalmology Assuit University Hospitals
Presenting history Presenting history Previous ocular history Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History Three weeks prior to presentation , the patient began to develop cloudy vision, photophobia and increasingly severe pain in the right eye (OD). Despite topical antiobiotic therapy at an outside facility.On Gatifloxacin and Tobramycin drops every hour and cyclopentolate 1% twice a day, OD. Despite this therapy, the ulcer in the right eye persisted and was worsening. 39-year-old white male contact lens wearer is complaining of cloudy vision, photophobia, and a red, painful right eye. History There is no history of other system affection. The patient is a contact lens wearer who has used disposable soft contact lenses for the past 3 months
Previous ocular history Previous ocular history Presenting history Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History The patient had switched to disposable soft contact lenses 3 months prior to presentation. History
Presenting history Previous ocular history Past medical history Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History History Mild hypertension and hypercholesterolemia
Presenting history Previous ocular history Trauma & operations Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History No history of trauma. No history of previous operations. History
Presenting history Previous ocular history Therapeutic history Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History Topical Gatifloxacin and Tobramycin every hour, OD, as well as cyclopentolate. His systemic medications included Valsartan and Atorvastatin. History
Presenting history Previous ocular history family & social history Past medical history Trauma & operations Therapeutic history family & social history History Noncontributory History Rare social consumption of alcoholic beverages. Patient is a non-smoker.
Blood pressure Blood pressure Pulse Temperature Head & neck Other systemic exam Systemic examination Examination 130/80 mmHg
Blood pressure Pulse Pulse Temperature Head & neck Other systemic exam Systemic examination Examination 80 beats/min with regular rhythm
Blood pressure Temperature Pulse Temperature Head & neck Other systemic exam Systemic examination Examination The patient is afebrile.
Blood pressure Head & neck Pulse Temperature Head & neck Other systemic exam Systemic examination Examination No abnormality detected
Blood pressure Other systemic exam Pulse Temperature Head & neck Other systemic exam Systemic examination Examination No abnormality detected
Visual acuity External exam Slit lamp ex. Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination VA :Count Fingers at 30 cm OD , 6/6 OS Examination
External exam Slit lamp ex. External exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination OD: There was conjunctival injection & a few SPK. The anterior chamber was deep & quiet. The iris & lens were normal. Examination OS: normal.
Slit lamp exam Slit lamp exam Ext. exam. Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination • OD Examination • OS: Normal • Enlarged corneal nerves (radial perineuritis) are also seen on high magnification. There is conjunctival injection and the anterior chamber is filled with 3+ cells and 2+ flare reaction. • Keratic precipitates line the endothelium inferior to the ring infiltrate and there is a 0.5mm hypopyon. Small defects in the epithelium are present over the area of ring infiltrate • 4x4 mm stromal ring infiltrate with surrounding white blood cell (WBC) infiltration.
Pupils External exam Slit lamp exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination 5mm dark and 3mm light, OU with no relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) Examination
Motility External exam Slit lamp exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination Examination OD : Full OS: Full
IOP External exam Slit lamp exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination Examination OD: Digitally Normal OS: 18 mmHg Applanation tonometry
CornealSensation External exam Slit lamp exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination Examination OD : decreased; OS : normal
Fundus exam External exam Slit lamp exam Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination OD: Very difficult and hazy posterior view. OS: Normal disc, macula, vessels, and periphery. Examination
Epithelialscraping Multiple swab samples Epithelialscraping Laboratory investigations Lab investigations Double-walled cyst structures were seen within the epithelium
Multiple swab samples Multiple swab samples Epithelialscraping Laboratory investigations Lab investigations No secondary organisms grew
Provisional diagnosis Acanthamoeba keratitis Provisional diagnosis
Differential diagnosis Herpetickeratitis Bacterial keratitis Differential diagnosis Fungal keratitis Contact lens overwear and associated ischemia
Differential diagnosis Acanthamoeba Keratitis History Contact lens; disproportionate pain Differential diagnosis dense infiltrate or classic "ring infiltrate", perineuritis, intense injection, some with keratouveitis, with or without epithelial defect Histopathoalogy Confocal Microscopy
Differential diagnosis Herpetic keratitis No recurrent attacks Differential diagnosis Mild to moderate pain No skin affection Morphology of the ulcer
Differential diagnosis Bacterial keratitis History (no improvement on antibiotic) Differential diagnosis culture
Differential diagnosis Fungal keratitis History: no history of plant trauma Differential diagnosis culture morphology
Differential diagnosis Contact lens overwear and associated ischemia Differential diagnosis history
Management Medical surgical Management Nonspecific 1-stop contact lens wear. 2-cycloplegic. 3- Steroid therapy. Specific 1-Aminoglycosides 2-Aromatic diamide 3-biguanide 4-imidazoles Epithelial debridement Penetrating Keratoplasty
Lines of management(cont) Followed by around the clock topical therapy initially, then slowly decreasing therapy with improvement Role of IV diamide therapy (pentamidine) in resistant cases is yet to be determined, but was adjunctive in this case report • Usually Biguanide(chlorohexidine 0.02% or polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) 0.02% every hour) • Plus or minus addition of diamide (propamidine isethionate (Brolene) 0.1% or hexamidine) Ongoing treatment Taper the treatment. Relapse is common. Treatment is prolong (20- 40wks) Epithelial debridement Cycloplegia for comfort with Cyclopentolate 1% BID or Atropine QD Steroid therapy (oral or topical) may help control inflammation after control of the infection has been achieved. Management Penetrating Keratoplasty (PKP) may be required in cases of impending perforation or for visual rehabilitation after scarring Be wary of recurrence with peripheral limbal cyst reactivation and infection of the graft. Continue topical anti-amoebic therapy. ? Oral as an adjuct has been helpful Oral Itraconazole or Ketoconazole 200-600mg/day (divided BID)
Slit lamp exam Slit lamp exam Ext. exam. Pupils Visual acuity IOP CornealSensation Motility Fundus exam Ophthalmic examination Examination
THANKS FOR YOUR KIND ATTENTION