Slavery Divides the Nation
520 likes | 794 Views
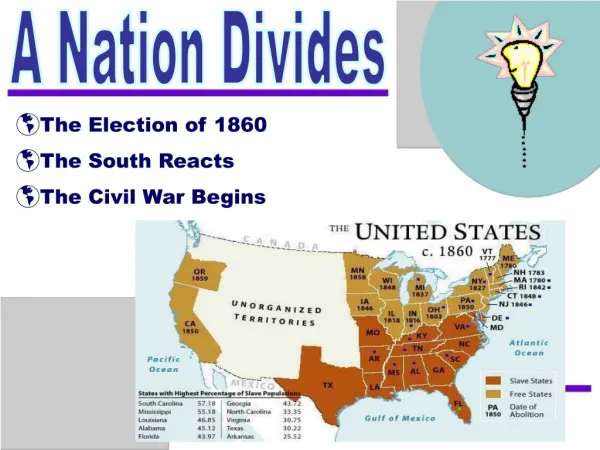
Slavery Divides the Nation. Missouri becomes a State. By 1819— 11 free states and 11 slave states Missouri applies for statehood as a Slave State Creates Crisis. Missouri Compromise, 1820. The Compromise Maine would enter as a free state Missouri would enter as slave

Slavery Divides the Nation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Missouri becomes a State • By 1819—11 free states and 11 slave states • Missouri applies for statehood as a Slave State • Creates Crisis
Missouri Compromise, 1820 • The Compromise • Maine would enter as a free state • Missouri would enter as slave • Congress draws an imaginary line dividing Louisiana Purchase • 36° 30 line • North of line Free • South of line Slave
Slavery Debate • North • South • Moderates2—Sides • Extend Missouri Compromise Line West • Have Popular Sovereignty—Let new states decide for themselves
Free-Soil Party • Created by members from Democrat and Whig Parties • Main GoalKeep slavery out of West • Party proved that slavery became a national issue
California • 184915 free states & 15 slave states • 1850California enters as free state • 3 other territories may join union as free states • South threatens to leave US
Compromise of 1850 • Five Parts • California enters as free state • New Mexico & Utah would decide by popular vote • Slave trade banned in Washington D.C. • Fugitive Slave Act • Border dispute between New Mexico & Texas settled
Fugitive Slave Act • Required all citizens to help catch runaway slaves • Made abolitionists feel part of the slave system
Uncle Tom’s Cabin1852 • Discussed the evils of slavery and injustice of fugitive slave act • Made slavery a moral problem
HarrietBeecherStowe “So this is the lady who started the Civil War.” -Abraham Lincoln
Crisis Worsens • Kansas-Nebraska Act • Proposed by Stephen Douglas • Louisiana Purchase divided into 2 pieces • Kansas • Nebraska • Issue of slavery decided by popular vote • South happy • North isn’t
Violence Erupts • People vote illegally • Proslavery government created • Anti-slavery settlers create their own government • Kansas in chaos
Bleeding Kansas, 1856 • Proslavery and anti-slavery groups attackeachother • John Brown brutally murders 5 slave supporters • Attack leads to moreviolence • 200 people killed
Bleeding Kansas, 1856 Border “Ruffians”(pro-slavery Missourians)
Dred Scott v. Sanford • Supreme Court case that determined: • Slaves are property • Congress did not have the power to outlaw slavery in any state • Southerners Rejoice!! Slavery legal everywhere
John Brown’s Raid • Planned a raid on a Federal Arsenal in Virginia • Wanted to distribute weapons to slaves • Doesn’t happen • Captured, found guilty of murder and treason • Sentenced to death
John Brown: Madman or Martyr Mural in the Kansas Capitol buildingby John SteuartCurry)
The Republican Party • Party created by politicians who opposed slavery
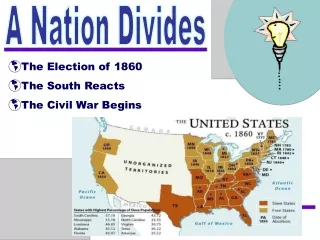
Election of 1860 • Lincoln (R), wins!! • South believes that they no longer have a voice in government • Only choice is to secede from union
The Nation Divides • December 20, 1860 South Carolina is the first state to leave the union • Six other states follow.
The Confederacy • The Confederate States of America • Seven states met in Alabama to form a new nation • President Jefferson Davis
John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry • Planned a raid on a Federal arsenal • Wanted to distribute weapons to slaves • Didn’t happen: Brown and his men were mostly captured or killed within 36 hours • Brown was ultimately hanged
Compromise of 1850 • California wants to be a free state • But the South assumed it wouldn’t be So. . . • California will be free, BUT • Utah and New Mexico will vote on slavery • Fugitive Slave Law: meant to appease South; many Northerners feel it turns them into slave-catchers. . .
Kansas-Nebraska Act 1850 • Proposed by Stephen Douglas • People in Nebraska Territory will vote on whether to have slavery or not (popular sovereignty) Sounds like a good idea, BUT • Anti-slavery (Freesoilers: poor farmers who couldn’t compete with slave-owners) and pro-slavery forces stream in. . . • Mini- civil war: “Bleeding Kansas”
John Brown • Abolitionist • Involved in the Underground Railroad • Moves to Kansas to support the anti-slavery cause • Responds to violence by proslavery men by organizing the murder of 5 proslavery settlers: Pottowatomie Creek Massacre
Today’s Question Abraham Lincoln called Brown a “misguided fanatic.” Do YOU think John Brown was a “misguided fanatic?” Misguided: confused Fanatic: extremist
Civil War Begins • Lincoln pledges no war unless started by South • Davis orders Confederate Army to seize federal forts, offices, property • Fort Sumter • Commander refuses to surrender • Confederacy attacksfort SumterSum • War Begins!!
The Civil War Ends • The Union sensed victory was near shortly after Gettysburg • Nov. 1864: Lincoln wins re-election • Feb. 1865: Congress passes the 13th Amendment, ending slavery. • April 1865: General Robert E. Lee surrenders to General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox, Virginia • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=chDhBTUyTeg
The Assassination of Abraham Lincoln • April 14, 1865: President Lincoln is assassinated by John Wilkes Booth • Assassination: The planned murder of an important individual, generally for political purposes.
Reconstruction (1865-1877) • A government program to repair the damage to the South and restore the Union • Many Southern cities destroyed • Over 600,000 dead • 4 million newly freed slaves • Poor whites lose jobs to freedmen migration • Planters lose labor and Confederate $ now worthless
Reconstruction Plans Abraham Lincoln’s 10% Plan for Reconstruction Andrew Johnson’s Presidential Reconstruction Similar Pardons, many personal given to military-political leaders No 10% requirement States required to officially abolish slavery within their state laws and pay back debt Even more generous to South • Pardon (forgiveness for a crime) to those willing to pledge allegiance • No pardons for military and government officials • Once 10% of a state’s citizens swore allegiance, they could create a new state constitution • Set tone of forgiveness
Impact on African Americans • March 1865: Freedmen’s Bureau created as first federal relief agency • Provided food, clothing, medical care and education • Black Codes: Laws restricting rights of freedmen • Curfews, Labor contracts, land restrictions • 14th/15th Amendments: Gave equal protection of laws, and voting rights to black men • High black populations lead to many freedmen being elected to public office during the 1870’s
Impact on the South & Presidency • Reconstruction Act of 1867: Placed Northern generals in charge of South • Required States to allow qualified blacks to vote (backed by 15thAmendment) • Required equal protection of laws • Leads to emergence of KKK • President Johnson nearly escapes impeachment (The removal of a President or Federal judge) for firing Secretary of War without Senate approval • Loses Republican nomination to Ulysses S. Grant, union general who wins 1868 election.
The End of Reconstruction: • Corruption in state & national government • Economic problems took place of movement for racial equality • Violence and intimidation to undermine new laws protecting blacks • Democrats make gains in Congress and help to get rid of Republican Reconstruction • Compromise of 1877: Gave Rutherford B. Hayes the Presidency in exchange for removal of federal troops
Reconstruction: Success or Failure? Successes Failures Allegiance not legit Many southerners find ways to limit rights of blacks. Racism continues Many southerners, white and black, remain in poverty • Union restored • 14th & 15th Amendments • Freedmen’s Bureau • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GJXT50QVGU0