THE TRUNK and SPINAL COLUMN
460 likes | 832 Views
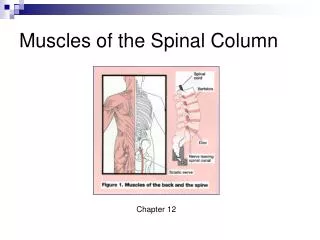
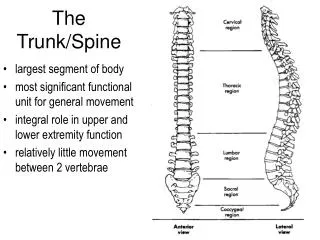
THE TRUNK and SPINAL COLUMN. Chapter 12. Bones of the Spinal Column. 33 bones, 24 are flexible A. Cervical - 7 B. Thoracic - 12 C. Lumbar - 5 D. Sacrum - 5 (false vertebrae - fused together) E. Coccyx - 4 (false vertebrae - fused together) LINK. Click on picture.

THE TRUNK and SPINAL COLUMN
E N D
Presentation Transcript
THE TRUNK and SPINAL COLUMN Chapter 12
Bones of the Spinal Column 33 bones, 24 are flexible A. Cervical - 7 B. Thoracic - 12 C. Lumbar - 5 D. Sacrum - 5 (false vertebrae - fused together) E. Coccyx - 4 (false vertebrae - fused together) • LINK Click on picture
General Landmarks 1. Spinous process 3. Transverse process - tubercle of rib articulates 5. Body 6. Vertebral foramen
General Landmarks • Vertebral notch • Superior • Inferior
General Landmarks • Intervertebral foramen
Cervical Vertebrae • First 7 vertebrae • Identified as C1 – C7 • C1 = Atlas • C2 = Axis
Atlas (C1) • Large vertebral foramen • Transverse ligament Anterior Posterior
Axial (C2) • Odontoid process or Dens
Note the differences: • Transverse process • Spinous process • Body
Note the differences: • Transverse process • Spinous process • Body
Actions of the Spinal Column • Flexion • Extension • Lateral Flexion • Rotation • Same side • Opposite side
Flexion Cervical flexion 1. Free in all three regions 2. Cervical and thoracic curves may be reduced to straight lines 3. Lumbar curve may be reversed in flexible subjects Lumbar flexion
Extension Cervical extension 1. Free in all three regions 2. Cervical and thorasic curves may be reduced to straight lines 3. Lumbar curve may be reversed in flexible subjects Lumbar extension
Lateral flexion Cervical lateral flexion 1. Free in cervical and lumbar regions 2. Limited in thorasic region by rib attachments 3. Accompanied by torsion Lumbar lateral flexion
Rotation Cervical rotation 1. Freest at top, least free at bottom 2. Accompanied by slight lateral flexion Lumbar rotation
Atlantooccipital joint • Articulation between the head and neck • i. Atlas (C1) • ii. Occipital bone • Acts as a hinge joint;flexion and extension • No rotation at this joint
Atlantoaxial • Articulation between C1 and C2 • a. pivot joint - rotation is here • b. the dens or ondontoid process fits into the inner, anterior portion of the vertebral foramen • with the help of the transverse ligament.
Arthordial or gliding-type joints • Composed of the synovial joint between superior and inferior articulating surfaces
Cartilaginous or synarthrodial joints • Intervertebral disks • i. nucleus pulposus - gel • ii. annulus fibrosus - covering • Shape and thickness varies with location • Make up approximately 25% of the column length • Allow limited motion in all three planes
Kyphosis - hunchback • Increase anterior concavity ( or curvature) of the thoracic curve
Lordosis - swayback • Increase posterior concavity of the lumbar region. • it causes shortened back extensors • it causes lengthened abdominal
Scoliois • Lateral curvatures or sideward deviations of the spine. • Decreases the ability of the spin to support the body • Distorts the body cavity and that crowds the organs • Puts pressure on the nerves • Causes: • Imbalance of the deep back muscles and ligaments
Scoliois • Treatment • Body cast • Electrical stimulation of deep muscles • Harrington Rod implant - ratchett effect
Ribs • 12 pairs • 7 pair are ‘true’ ribs • 5 pair are ‘false’ ribs • 3 pair attach indirectly to the sternum • 2 pair are ‘floating ribs’ that don’t attach to the sternum