Enhancing E-commerce Sales through Consumer Behavior Insights
210 likes | 331 Views
Explore the impact of consumer behavior on e-commerce sales and strategies to improve customer experience, driven by personalized interactions and community engagement.

Enhancing E-commerce Sales through Consumer Behavior Insights
E N D
Presentation Transcript
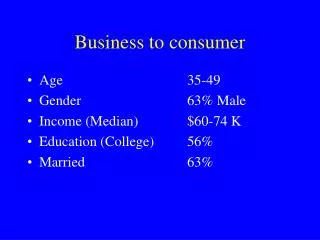
Business to consumer • Age 35-49 • Gender 63% Male • Income (Median) $60-74 K • Education (College) 56% • Married 63%
E-commerce sales by categories Category Sales ($B) Growth (1yr) Orders Total 6.28 205 % 71.3 Computer goods 2.84 194 % 14.13 Entertainment 1.28 290 % 28.86 Consumer goods 0.73 206 % 9.06 Gifts 0.61 347 % 10.26 Apparel 0.50 152 % 5.06 Food/Wine 0.25 44 % 3.18 Home/Garden 0.06 274 % 0.73
What is driving business? • Referral sources - • Web 50% (email - 18.5%, AOL -16%) • Friend/WOM - 30% • Offline experience w/retailer - 30% • Print - 15% (especially catalogs) • TV - 2.4% • Radio - 1%
Day of week • Offline retailers - peak on Sat/Sun • Online - fairly even throughout the week • Slowest days are Sat/Sun • sales decline as week progresses
Importance weights • Product representation • prices • selection • delivery • ease of ordering • information • customer support • shipping and handling • privacy policy • navigation and looks Teens, young adults, average income adults with no kids Price most important For mature adults, gift buyers 1. product representation 2. customer support .. 5. price
Consumer Behavior • Expectations have changed • Expect customized products • Want full access to own account information • Want the experience to be fun and entertaining • Want to interact with the ad, not just read it • Opportunities • personalization • community building • interaction
Interactivity • Depends on: • Direct communication • Individual choice • Friendly technology
Consumer Behavior Impact of interactive site = increased usage • Frequent use of service • Invest more time to understand site capabilities • Increase duration of online activities Real World • Charles Schwab: 20% increase in revenue and 30% increase in profits after going online
Communication Methods Broadcast Direct Targeting Dialogue
Communication Trend Dynamic Personal Impersonal Static
Individual Choice • Unlimited choice produces information processing overload • Need for organization and suggestion to simplify task • Consumers need selection and suggestion • Selection + Suggestion = Value
Selection and suggestionSheth and Sisodia (1997) • Selection • Greater value consciousness • Power shift to consumers • Shopping on demand • Suggestion - increases loyalty • Greater personalization • Co-creation • Automation of consumption
Similarities • Media = real lifeReeves and Nash • People treat machines and software just like people • Politeness • Personality • Gender bias • Media quality
Differences • Lack of social cues • Group dynamics • Flaming - speak incessantly on relatively uninteresting subject or with a patently ridiculous attitude • Why is there more flaming in email communications ? • Lack of feedback - harder to judge disapproval and confusion • Text is not as rich as personal interaction - need to use stronger words and images • Lack of social cues and anonymity - causes people to be braver • Implication for customer service
Differences • Quality cues • How to communicate quality • Hanson and Putler (96) varied the number of downloads • Need for independent verification • Cognitive difficulty • Keyword search or browse or both ?
Value of Online CommunitiesHagel and Armstrong • Communities of transaction • buy, sell, deliver info e.g. Virtual Vineyards • Communities of Interest • Special topics, high degree of interpersonal communication, e.g. GardenWeb, Motley Fool • Communities of fantasy • Red Dragon Inn, ESPNet • Communities of relationship • life experiences, cancer forum, divorce • Try to provide all four as far as possible - travel industry - source of long term first mover advantage
Online Communities – Advantages • encourage communication • Message boards, chat rooms, instant messaging • focus social interaction • Members log in for hours a day vs. minutes • Businesses are active community builders • Improves organization’s communication ability • Virtual gathering places provide power to consumer • Online communities can alter the nature of marketing
Online Communities – Disadvantages • isolate individuals • Typing at a keyboard isn’t real socializing • lead to psychological problems • Depression, loneliness • lead to shallow relationships
Designing the community • Narrow focus - small size • Broad market - less passionate interaction
Operating the community • Executive moderator • manage large number of system operators • moderate discussions • transform low quality to intense interaction • Community merchandiser • Executive editor - programming, external content • Archivist • Usage analyst • New product developer