Calculating Electrical Power and Energy Consumption in Circuits**
110 likes | 253 Views
This article provides insights into calculating missing quantities in electrical circuits, focusing on power (P), voltage (V), and current (I) relationships. It explains the formulas used for determining electrical power and energy consumption, highlighting the significance of the watt (W) and joule (J) as units of measurement. Through various examples involving circuit components like batteries, bulbs, and heaters, readers will learn how to apply the principles of electricity to practical scenarios and compute energy costs for household appliances.

Calculating Electrical Power and Energy Consumption in Circuits**
E N D
Presentation Transcript
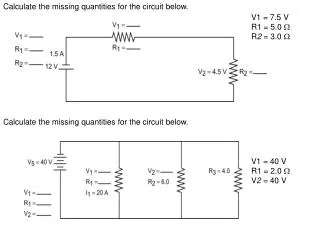
Calculate the missing quantities for the circuit below. Calculate the missing quantities for the circuit below. V1 = 7.5 V R1 = 5.0 R2 = 3.0 V1 = 40 V R1 = 2.0 V2 = 40 V
9.2 The Power of Electricity Pg. 320 • Electrical power is the rate at which electric potential energy is being transformed. • One watt (W) of power is one joule (J) of electric potential energy transformed in one second 1W = 1J/s • Electrical power (P) be calculated by multiplying voltage (V) and current (I) • P=V∙I • The amount of electrical energy (E) used by a device is its power consumption (P) multiplied by the length of time (t) the device is turned on • E = Pt • Since the joule (J) is a very small amount of electrical energy, the kilowatt-hour (kW∙h) is used for devices that consume larger amounts of energy • How much energy is used to dry someone’s hair using a hair dryer? • the same amount of energy needed to lift an average student 1.5km into the air.
Electrical power (P) is the rate of change in electrical energy • and the rate at which work is done or energy is transformed. • The unit for measuring energy is the joule (J), named for the British scientist James Prescott Joule (1818-1889). • One watt (W) of power is one joule (J) of energy transformed in one second (s) • 1W = 1J/s • named in honour of Scottish inventor James Watt (1736 – 1819) • James Watt invented the unit of power called “horse power” to compare the power of his improved steam engine to the power of a horse, to help boost sales. • One unit of horsepower is 746 W
CALCULATING ELECTRICAL POWER p.323 If a 6.0V battery supplies a current of 2.0A, what is the power output of the battery? A current of 5.0 A flows through a flashlight bulb when it is connected to 6.0 V. What is the power of this bulb? Q43. A 600 W electric heater is connected to a 120 V source. What current flows through the heater? Example Power (P) = voltage (V) x current (I) P = V x I P = 6.0V x 2.0A P = 12.0W
A 2.5 A current flows through a 100 W lamp. What is the voltage across the lamp? What is the current through a 6.0 W light bulb when it is connected to a 1.5 V battery? A 40 W light bulb is connected to a power supply and draws a current of 0.75 A. What is the voltage of the power supply? (b) If the 40 W light bulb is replaced by a 100 W light bulb, how much current will flow through the 100 W bulb?
A power rating is a measurement of how much electrical energy an electrical device consumes for every second it is in use 1.0 W is the transfer of 1.0 J of energy every second (W=J/s) For example, a 60 W light bulb uses 60 J of electrical energy each second (60 W = 60 J/s)
Calculating Energy ConsumptionPg. 324 You can calculate the amount of electrical energy (E) a device consumes by multiplying the power rating (P) with the amount of time (t) the device is used for. Time (t) is always calculated in seconds (s) P = E/t E = Pt Example How much electrical energy is consumed by a 1400W hair dryer it if is used for 5.0min? E = Pt E = 1400W x 300s (5 x 60) E= 420 000 J or 4.2 x 105 J
How much energy, in joules, is consumed by a 75 W light bulb if it is left on for 30 min? How much energy, in joules, is consumed by the typical triple strand xmas tree lights that use 25 W per strand and are left on for 6 hours? How much energy, in joules, is consumed by a 500 W stereo if it is left on for 4.0 h?
A Larger Unit for EnergyPg. 325 A kilowatt-hour (kW∙h) is the product of power in kilowatts and time in hours 1000 W = 1kW As you might notice, most electrical devices consume many joules of electrical energy. In terms of electrical energy, the joule is a very small amount The power company that supplies electricity to your home keeps track of the electrical energy you consume Your home has a meter that keeps track of how much electricity is used, and there is a meter-reader that comes to read it to determine how much energy has been consumed since the last bill
The Cost of ElectricityPg.325 A meter reader determines that a business has used 6525 kWh of energy in two months. If electricity costs 10¢ per kWh, calculate the bill. A 500 W stereo is used in a household. Electricity costs 8¢ per kWh. How much does it cost to operate the stereo 3.0 h a day for 30 days? The average home will use more than 50 strings of xmas lights each season and each strand uses 25 W which are left on for roughly 8hrs a day. If electricity costs 8¢ per kWh, how much will it cost to have those lights on for a month?