MEMS vibratory g yroscope
160 likes | 715 Views
MEMS vibratory g yroscope. by Nikul Jani. Contents. Introduction to MEMS devices How the gyroscope works? How the MEMS Gyroscope is different? Structure of MEMS Gyroscope Mathematical model for to calculate angular rotation occured Some other designs References.

MEMS vibratory g yroscope
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MEMS vibratory gyroscope by Nikul Jani
Contents • Introduction to MEMS devices • How the gyroscope works? • How the MEMS Gyroscope is different? • Structure of MEMS Gyroscope • Mathematical model for to calculate angular rotation occured • Some other designs • References
Red blood cells (30 micron) (range of size :0.1 to 100 micron) Human hair (50 micron) Micro Electro- Mechanical System MEMS Gyro-sensor http://www.digikey.com/US/EN/techzone/sensors/resources/articles/MEMS-Accelerometers.html
What are the MEMS devices? Device in which mechanical behaviour of links interacts with microelectronics 4 Basic parts of MEMS • Micro sensors • Micro actuators • Micro Electronics • Micro structures
Some of the Applications • Accelerometers • Gyro sensors • Magnetometers • Microphones • Microfluidics • Bridge to Nanotechnology http://electroiq.com/blog/2013/10/mems-devices-for-biomedical-applications/
Conventional Gyroscope • It is a device which measures the rotations • The conventional gyroscope • problems with the conventional types • Where it is used? • Aerospace applications • Aircrafts and Automobiles • Robotics, camera
How it works? • Principle of operation is Coriolis effect • Statement • If the object having rotary motion is displaced in the plane of rotation then it will be accelerated in the direction perpendicular to plane of motion. • Taking the direction of rotation as per left hand rule.
How the MEMS gyroscope is different? • Same principle is applied but in the reverse manner. • Here vibratory motion is given continuously. Any rotation is the disturbance that causes displacement. http://fourier.eng.hmc.edu/e80/inertialnavigation/node3.html Displacement of the right mass, Inertia force due to coriolis effect is, If we are allowing the mass to move,
Overview of the structure when capacitance is taken as first output • A simple model for the yaw angle measurement • D electrodes supplies vibratory energy • S electrodes senses the change in displacements http://memscentral.com/Secondlayer/mems_motion_sensor_perspectives-2.htm
Solution for the simple model Damped natural frequency for X directional motion Damped natural frequency for the y directional motion Phase lag with X directional motion for equation of motion in the y direction, Solving the above equation, When both frequency matches highest amplitude can be got.
Some comments on the simple model • Linear model needs modification for non-linearity. • For the multi axis gyro this model is not valid • Sensitivity to temperature, so calibration is required
Sensor Readout of primary and secondary positions • The value of the positions are the outputs from the mechanical functionality • what need to be sensed for various kinds of designs • Capacitance for this kind of design • resistance for piezoresistive design • voltage
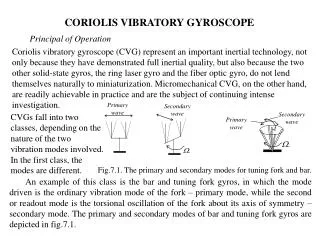
Some other designs • Pizeoelectric gyroscopes • A vibrating membrane responses under coriolis effect • Tuning fork gyroscope • simple structure is shown in slide 8 • Cylindrical resonator gyroscope (CRG)
Some problem to the devices • These devices are very sensitive to temperature and packaging(how it is packed). • The system can be non linear for some value of inputs Change of gain in MEMS gyroscope with temperature variation http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924424708005682#
Summary A quick Intro MEMS devices Working principle of conventional MEMS Gyroscope Structure of MEMS Gyroscope Mathematical derivation for angular rotation Some other designs
Reference https://www.mems-exchange.org/MEMS/what-is.html http://clifton.mech.northwestern.edu/~me381/project/done/Gyroscope.pdf http://nptel.ac.in/courses/105106116/4 http://nptel.ac.in/courses/117105082/27 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924424708005682# http://www.st.com/web/en/catalog/sense_power/FM89