Fiedler Contingency Model
200 likes | 779 Views
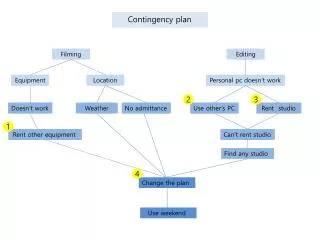
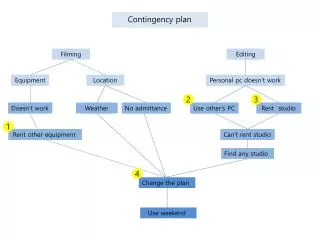
Fiedler Contingency Model. Business Management 12. Contingency Model. The group performance depends on the match between the leader’s style, interaction with his/her followers and the degree to which the situation gives the leader control and influence.

Fiedler Contingency Model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fiedler Contingency Model Business Management 12
Contingency Model • The group performance depends on the match between the leader’s style, interaction with his/her followers and the degree to which the situation gives the leader control and influence. • Least Preferred Co-Worker (LPC) Questionnaire, measures the two different leadership styles.
Findings • Evaluation of three contingency variables • High control situation • Low control situation
Fixed Leadership Orientation • Fixed, unchanging. • Relationship orientated leadership. • Task orientated leadership.
Three Contingency Dimensions • Leader-member relations. • Task structure. • Position power
Improving Effectiveness • 2 ways • Changing the type of leader to fit the situation. Ex: Bringing a task-oriented leader as a replacement. • Change the situation to fit the leader. Ex: Restructuring tasks, increase or decrease in things like promotions and disciplinary actions.
Criticisms • Problems with the LPC, and the practicality of it. Unrealistic to think a leader could not change their style. • More variables needed to fill in some gaps in the model. • Variables were difficult to assess. • Effective style needs to reflect situational factors.
Examples • Natural disasters, floods or fires. • Research Scientists