Neuse Estuary Eutrophication Model
90 likes | 121 Views
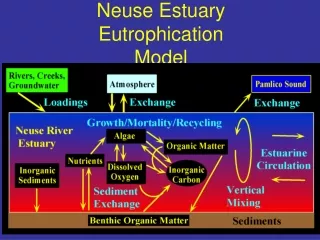
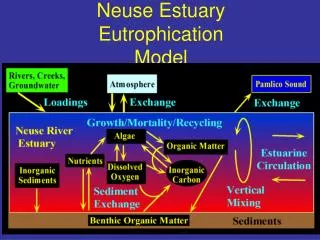
Neuse Estuary Eutrophication Model. Nitrogen Inputs. Cause and Effect Relationships. Algal Density. Chlorophyll Violations. River Flow. Carbon Production. Harmful Algal Blooms. Sediment Oxygen Demand. Frequency of Hypoxia. Duration of Stratification. Shellfish Abundance.

Neuse Estuary Eutrophication Model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nitrogen Inputs Cause and Effect Relationships Algal Density Chlorophyll Violations River Flow Carbon Production Harmful Algal Blooms Sediment Oxygen Demand Frequency of Hypoxia Duration of Stratification Shellfish Abundance Fish Health Number of Fishkills NeuBERN Bayes Net Estuary Model
Phytoplankton (Algae) Mass Balance (equation from the model proposed by Chen and Orlob (1972)) where: V = segment volume (m3) C1 = phytoplankton concentration (g/m3) Q = flow volume (m3/t) E = diffusion coefficient (m2/t) A = segment surface/bottom area (m2) µ1 = phytoplankton growth rate (t-1) R1 = phytoplankton respiration rate (t-1) s1 = phytoplankton settling rate (t-1) M1 = phytoplankton mortality rate (t-1) µ2 = zooplankton growth rate (t-1) C2 = zooplankton concentration (g/m3) F2,1 = fractional feeding preference
Parameter Selection Example: Phytoplankton Settling For phytoplankton settling, another common approach is to treat phytoplankton settling as a velocity term with an areal loss: (Chapra and Reckhow 1983, Chapter 14) phytoplankton settling (mass/time) = v1AC1
Table 1. Phytoplankton settling velocities (Bowie et al. 1985)