Chapter 10
430 likes | 630 Views
Chapter 10. Pursuing Security. Thinking About Security. The Nature of Security. Drama and Dialogue of Insecurity Critiquing the drama. Conflict and Insecurity: The Traditional Road. War: The Human Record. Frequency Lower percentage of countries involved in international conflict

Chapter 10
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 10 Pursuing Security
The Nature of Security • Drama and Dialogue of Insecurity • Critiquing the drama
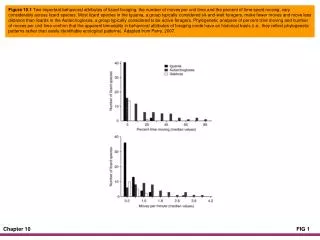
War: The Human Record • Frequency • Lower percentage of countries involved in international conflict • Higher percentage of countries involved in civil conflicts • 30 percent of all wars have occurred in last 200 years • Severity • 75 percent of all war deaths have occurred since 1900
The Causes of War • Force as a political instrument
Diplomatic and Psychological Impacts of Force • Spiralling insecurity • Temptation to use it • Expense (imperial overstretch thesis)
Levels of Violence: From Intimidation to Attack • Backdrop to diplomacy • Supply source to another government or insurgency group • Overt threat against an opponent • Limited demonstration of violence • Direct use of force to defeat an opponent
Effectiveness of Force • Measurement • Cost/benefit analysis • Goal attainment
Conditions for successful use of force • Clearly defined, long-standing, and previously demonstrated commitment • Strong commitments, publicly announced by leaders • Military force used to counter other military force, not to control political events • Force used early and decisively instead of through extended threatening and slow escalation • Clearly established goals • Secure domestic support for actions and goals
The Changing Nature of War • Technology has increased killing power • Nationalism has increased numbers and intensity of wars • Technology and nationalism have expanded scope of war • Strategy has changed • Power to defeat is the traditional goal • Power to hurt increasingly important
Classifying Wars • Local • Regional • Strategic nuclear conflict
Local Conflict • Arms Transfers • Destination and sources • Mostly to LDCs • Mostly from EDCs • After end of cold war, sales to LDCs decreased; United States became largest supplier
Motives • Supply allies during peacetime • Intervene in conflict • Gain diplomatic influence over recipient • Keep arms industry operating to preserve defense production infrastructure • Profit
Dangers to importing countries • Instability leads to arms sales, which leads to more instability • Cost of weapons diverts funds from domestic programs
Dangers to suppliers • Moral corruption • Identification with recipient can lead to higher involvement • Possibility of facing one's own weapons (black market) • Hard to persuade others not to do what you are doing
Covert Intervention and Terrorism • Increase in civil strife • Use of guerilla tactics • Growth of international terrorism • World Trade Center and Pentagon attacks • Possible solutions • Success of terrorism
Direct Military Intervention • High costs • Possibility of failure • Possibility of escalation • Questionable legitimacy
Regional Conflict • Avoiding unchecked escalation • Keep communication open • Limit goals • Restrict geographical scope • Observe target restrictions • Limit weapons • NBCs
Strategic Nuclear War • The Continuing Role of Nuclear Weapons • Backdrop to power
How a Nuclear War Might Start • Irrational leader • Unprovoked attack • Last-gasp defense • Accident • Error of judgment • Escalation • Multipath scenarios
Strategic Nuclear Weapons and Strategy • Fundamental goals determining selection of weapons • Minimize chance of war • Maximize chance of survival
Deterrence • Capability • Credibility • MAD versus NUT strategies
Domestic Security Mechanisms • Norms against violence • Security forces • Disarmament • Conflict-resolution
International Security • Unlimited self-defense • Limited self-defense through arms control
Arms limitations: Numerical restrictions • SALT I & II • START I & II
Development • Antiballistic Missile (ABM) Treaty • Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT) • Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT)
Deployment • Anti-Personnel Mine (APM) Treaty
Arms Reductions • Categorical restrictions • Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty
Nonproliferation • Transfer restrictions • Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)
Barriers to Arms Control • Security Barriers
Caution about the current political climate • End of cold war offers opportunity to reduce arms • Realists not persuaded to abandon military approach • Cannot predict future U.S.-FSRs relationship • Increased Chinese power • Proliferation of “weapon states”
Caution about the claimed contributions of arms control • Realists doubt that arms set off an arms race • Skeptics doubt that reducing arms will increase security
Technical Barriers • How to compare weapons systems • Verification difficulties • Break-out cheating • Creep-out cheating • On-site inspection • Absolute versus adequate verification
Domestic Barriers • National pride • Military spending and the economy • Arguments that it hurts the economy • Arguments that it helps the economy
International Security Forces: National and International Security • Defining security • Organizing security • Global • UN • Regional • Organization for Security and cooperation in Europe (OSCE) • Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
Collective Security: Similar to domestic law enforcement • Force used only in self-defense • Peace is indivisible • Unite to halt aggression and restore peace
UN peacekeeping: Passive/reactive • Most efforts in LDCs • In the past, used military contingents from smaller, nonaligned powers • With the end of the cold war, increasing UN security role for larger powers
UN peacemaking • More aggressive posture • Barriers • Lack of financial support
International security and the future • Frustrations with UN • Controversy • May be a necessity
Abolition of war • Disarmament • General and complete disarmament (GCD) • Unilateral • Negotiated • Pacifism • Universal • Private • Antiwar