Procedures
380 likes | 604 Views
Procedures. Basic Format Myringotomy & Tympanostomy. ENT FACT QUIZ: AAO-NHS*. Test your knowledge of common ear, nose and throat disorders and their treatment . Cotton swabs are a safe and easy way to clean wax from inside your ears. Fact or Fiction

Procedures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Procedures Basic Format Myringotomy & Tympanostomy
ENT FACT QUIZ: AAO-NHS* • Test your knowledge of common ear, nose and throat disorders and their treatment. • Cotton swabs are a safe and easy way to clean wax from inside your ears.Fact or Fiction 2. Reading in a moving car can cause motion sickness (make you "car sick").Fact or Fiction 3. Hay fever is not caused by hay and does not cause a fever.Fact or Fiction 4. Tonsils and adenoids filter bacteria out of what we swallow and breathe.Fact or Fiction * American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
ENT FACT QUIZ 5. A person can be trained or conditioned not to snore.Fact or Fiction 6. You can "toughen up" your ears by continued exposure to loud noise.Fact or Fiction 7. You should avoid speaking or singing when your voice is hoarse.Fact or Fiction • You don't have to go swimming to get "swimmer's ear."Fact or Fiction
Objectives • Assess the anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of the myringotomy, tympanostomy. • Analyze the diagnostic and surgical interventions for a patient undergoing a _______________. • Plan the intraoperative course for a patient undergoing_____________. • Assemble supplies, equipment, and instrumentation needed for the procedure.
Objectives • Choose the appropriate patient position • Identify the incision used for the procedure • Analyze the procedural steps for_____________. • Describe the care of the specimen • Discuss the postoperative considerations for a patient undergoing _______________ .
Terms and Definitions • Otitis Media • Pressure Equilization Tubes (PE Tubes) • Also called polyethylene ventilation tubes
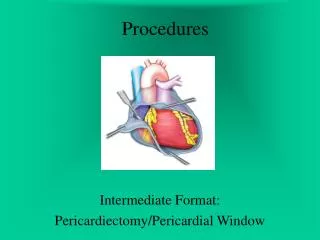
Definition/Purpose of Procedure • Incision into the tympanic membrane under direct vision to remove accumulated fluid—often to treat otitis media in the middle ear; PE tubes are frequently inserted through the tympanic membrane during this procedure
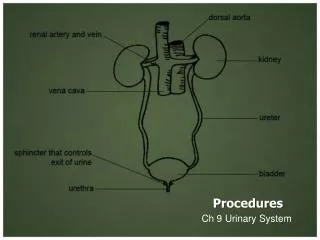
Pathophysiology: Deafness • Conduction-type • Sensorineural • Central deafness • Mixed-type • Functional • Congenital • Neonatal
Diagnostics • Exams • Otoscope • Preoperative Testing
Surgical Intervention:Special Considerations • Patient Factors • Peds: may warm room, toy or other distraction • Room Set-up • ENT microscope positioned near head of OR table –ready to be move once pt anesthetized • OR Table in reverse position to make room for microscope and sitting surgeon • Set up on Mayo stand
Surgical Intervention: Anesthesia • Method: Local, General inhalation for children (typical); can be performed under local in office for adults • Equipment
Surgical Intervention: Positioning • Position during procedure • Supine with head turned (surgeon will do) • Supplies and equipment • Special considerations: high risk areas
Surgical Intervention: Skin Prep • Method of hair removal • Anatomic perimeters • Solution options
Surgical Intervention: Draping/Incision • Types of drapes • 4 cloth drapes typically or fenestrated drape • Order of draping • Special considerations • Clean procedure; use best clean technique • State/Describe incision • Tympanic membrane
Surgical Intervention: Supplies • Specific • Suture: N/A • Medications on field (name & purpose) • Antibiotic gtts (Cortisporin otic often used) • Catheters & Drains • Pressure equilization tubes specific to surgeon orders
Surgical Intervention: Supplies • General • Mayo stand cover • Suction tubing • Gloves • Fenestrated towel drape • 4 x 4 gauze • Disposable myringotomy knife • Small basin w/water • Pharaceuticals per orders
Surgical Intervention: Instruments • General • Specific • Myringtomy Tray
Surgical Intervention: Equipment • General: Suction apparatus • Specific: ENT Microscope with proper lens and ocular adjustment per surgeon specification • Sterile microscope hand grips • Sitting stool for surgeon
Surgical Intervention: Procedure Steps • Patient is positioned with head turned so that affected head is up • Patient is draped w/fenestrated drape or 4 towels (no prep) • Surgeon places microscope to visualize, and inserts aural speculum in ear canal • If wax accumulation, surgeon will remove w/curette • * estimate size of ear canal and present appropriate size speculum • * have gauze available to clean the wax off the curette • Surgeon makes small curved incision in the posterior-inferior quadrant of the tympanic membrane with a sharp ear (myringotomy) knife • * STSR careful to pass so that surgeon need not look away from operative site • Be ready for suction; keep tube patent by suctioning water through it or using stylet (middle ear fluid is thick) • *culture & sensitivity may be taken at this time from fluid • If fluid or pus is present, it is suctioned using it is suctioned using a Frazier or Baron suction tip
Surgical Intervention: Procedure Steps • Surgeon positions PE tube, which has been positioned on alligator ear forceps, into the incision (never with gloved hands due to powder) • * STSR grasps PE tube in the jaws of alligator forceps and carefully pass to surgeon
Surgical Intervention: Procedure Steps • Surgeon instills antibiotic drop, then packs with cotton ball • * Have cotton and med ready (circulator may instill gtts as convenient from med bottle) • Surgeon removes speculum • Patient’s head is turned, and procedure is repeated on other ear (if required) • * Be prepared to switch sides of OR table
Counts • Initial: usually N/A—per facility policy • First closing • Final closing • Sponges • Sharps
Dressing, Casting, Immobilizers, Etc. • Types & sizes • Cotton ball • Type of tape or method of securing
Specimen & Care • Identified as N/A • Handled: routine, etc.
Postoperative Care • Destination • PACU: Parent available once initial report give and VS stable • Outpatient Discharge—usually within an hour • Expected prognosis (Good) • Pt instructed to keep dry until PE tubes fall out or are removed and TM healed • Hearing expected to return to normal
Postoperative Care • Potential complications • Failure to resolve the ear infections. • Persistent perforation after the tube falls out of the eardrum. • Chronic ear drainage. • Need for further and more aggressive surgery such as tonsil, adenoid, sinus, or ear surgery. • Hearing loss. • Scarring of the eardrum.
Postoperative Care • Need to keep the ear dry and to use ear plugs. • Foreign body reaction to the tube itself - for example, an allergic reaction to the tube material (rare). • Pt may require second procedure to remove retained tube • Surgical wound classification: II
Resources • www.Allrefer.com • STST pp. 587-596, 601-612, 618-630 • www.nucleusinc.com • www.pedisurg.com • Alexanders pp. 733-736 • Fullers pp. 605, 608-609 • Goldman p. 435