Understanding Queues in C Programming: Definitions, Implementations, and Exercises
140 likes | 264 Views
This resource provides a comprehensive overview of queues as a linear data structure in C programming. It covers the fundamental concepts, including definitions of queues, FIFO (First-in, First-out) behavior, and the distinction between queues and stacks (LIFO). The material includes two different implementations of queues: with linked lists and fixed-size arrays. Through classroom exercises, students will learn how to add and remove items from queues and conduct necessary error checking. Ideal for CS-2301 programming students looking to grasp queue fundamentals.

Understanding Queues in C Programming: Definitions, Implementations, and Exercises
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Queues CS-2301 System Programming ConceptsHugh C. Lauer (Slides include materials fromThe C Programming Language, 2nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie,and from C: How to Program, 5th and 6th editions, by Deitel and Deitel) Queues
Definition – Linked List • A linear data structure in which each element contains a pointer to the next element • (Usually) has a beginning and an end • Items can (sometimes) be added anywhere • Beginning • Middle • End • Items can be removed from anywhere Queues
Note • Array is also a linear data structure with a beginning and an end • No pointers to next item • Implicit in ++ and -- operators • Very difficult to add items to beginning or middle! Queues
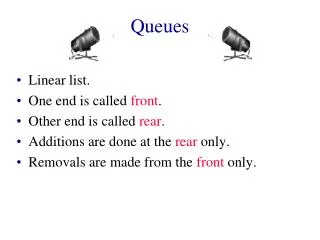
More Definitions • Queue:– a linear data structure in which items are always added to end and removed from beginning • FIFO:– First-in, First-out • Stack:– a linear data structure in which items are always added to the beginning and also removed from beginning • LIFO:– Last-in, First-out • Neither stacks nor queues need to be implemented via linked lists Queues
Programming Assignment #5(CS2301, B-term 11) • Provide two different implementations of a queue • Linked list • Fixed-size array • Note that fixed-size array cannot hold an arbitrarily long queue Queues
Queue.h #ifndef QUEUE_H #define QUEUE_H #include "Simulation.h" #if defined QUEUE_ELEMENT /* The actual interface definition for the queue begins here and uses QUEUE_ELEMENT as a type */ intqueueEmpty(void); /* returns TRUE if the queue is empty, FALSE if not */ intenqueue(QUEUE_ELEMENT e); /* Adds a copy of the argument to the tail of the queue. Returns TRUE if successful, FALSE if not */ intdequeue(QUEUE_ELEMENT *e); /* Removes the first element from the queue and stores it into the location pointed to by e. Returns TRUE if successful, FALSE if not */ intmaxQueueLength(void); /* Returns the maximum number of elements that have been stored in the queue at one time */ intcurrentQueueLength(void); /* Returns the number of elements currently in the queue */ // End of interface definition #endif#endif Queues
QUEUE_ELEMENT is defined in Simulation.h as typedefstruct customer Customer; #define QUEUE_ELEMENT Customer Queue.h #ifndef QUEUE_H #define QUEUE_H #include "Simulation.h" #if defined QUEUE_ELEMENT /* The actual interface definition for the queue begins here and uses QUEUE_ELEMENT as a type */ intqueueEmpty(void); /* returns TRUE if the queue is empty, FALSE if not */ intenqueue(QUEUE_ELEMENT e); /* Adds a copy of the argument to the tail of the queue. Returns TRUE if successful, FALSE if not */ intdequeue(QUEUE_ELEMENT *e); /* Removes the first element from the queue and stores it into the location pointed to by e. Returns TRUE if successful, FALSE if not */ intmaxQueueLength(void); /* Returns the maximum number of elements that have been stored in the queue at one time */ intcurrentQueueLength(void); /* Returns the number of elements currently in the queue */ // End of interface definition #endif#endif Queues
structlistItem {typeQUEUE_ELEMENT;structlistItem *next; }; structlistItem *head, *tail; • QUEUE_ELEMENT • QUEUE_ELEMENT • QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT next next next next Linked List Implementation Classroom exercise:– Add an item to tail ofnon-empty queue Classroom exercise:– Add an item to tail ofempty queue Lists and Trees
structlistItem {typeQUEUE_ELEMENT;structlistItem *next; }; structlistItem *head, *tail; • QUEUE_ELEMENT • QUEUE_ELEMENT • QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT next next next next Linked List Implementation Classroom exercise:– Remove an item fromnon-empty queue Lists and Trees
Fixed Array Implementation • If maximum queue length is always less than N, then we can implement the queue with an array of size N • How? Queues
Fixed Array Implementation (continued) … QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT • Classroom exercises:– • How to represent head of queue? • How to represent tail of queue? N Queues
Fixed Array Implementation (continued) … QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT QUEUE_ELEMENT • Classroom exercises (continued):– • How to add an item to the queue? • How to remove an item from the queue? • What error checking is needed? N Queues
Questions? Queues