Tree Data Structures: A Comprehensive Guide
540 likes | 575 Views
Learn about tree data structures, terminologies, ADT, traversal methods, and iterative implementations. Explore examples of trees in file systems, organization charts, and programming applications. Master the concepts of roots, internal and external nodes, ancestors, height, and subtrees. Dive deep into preorder and postorder traversals with hands-on demos. This comprehensive guide is ideal for beginners and advanced learners in computer science.

Tree Data Structures: A Comprehensive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
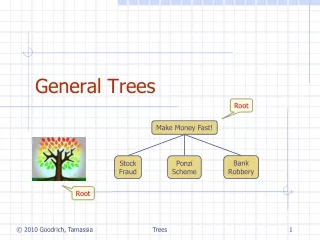
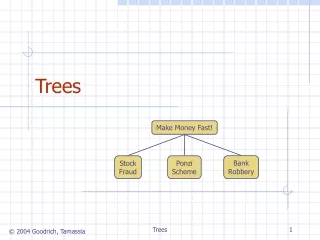
General Trees Root Make Money Fast! BankRobbery StockFraud PonziScheme Root Trees
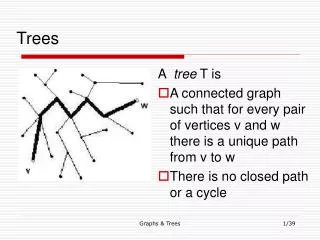
Computers”R”Us Sales Manufacturing R&D US International Laptops Desktops Europe Asia Canada What is a Tree Root • In CS, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure • A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child relation • Applications: • Organization charts • File systems • Function invocation in programming Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Tree Terminologies • Root: node without parent (A) • Internal node: node with at least one child (A, B, C, F) • External node (a.k.a. leaf): node without children (E, I, J, K, G, H, D) • Ancestors of a node: parent, grandparent, grand-grandparent, etc. • Depth (or level) of a node: number of ancestors • Height of a tree: maximum depth of any node • Descendant of a node: child, grandchild, grand-grandchild, etc. • Subtree: tree consisting of a node and its descendants Subtree Trees
Examples of Trees • File system • Internal nodes: directories (folders) • External nodes: files Trees
Tree ADT • Query methods: • boolean p.isRoot() • boolean p.isExternal() • Additional methods may be defined for specific applications • We use positions to access nodes • Generic methods: • integer size() • boolean empty() • Accessor methods: • position root() • list<position> positions() • Position-based methods: • position p.parent() • list<position> p.children() position = pointer list = linked list or vector Trees
Preorder Traversal • A traversal visits the nodes of a tree in a systematic manner • Preorder traversal: a node is visited before its descendants • Application: print a structured document AlgorithmpreOrder(v) visit(v) foreachchild w of v preOrder (w) 1 Quiz! Make Money Fast! 2 5 9 1. Motivations 2. Methods References 6 7 8 3 4 2.3 BankRobbery 2.1 StockFraud 2.2 PonziScheme 1.1 Greed 1.2 Avidity Trees
Preorder Traversal: Example • How to print this document? Trees
Postorder Traversal • Postorder traversal: a node is visited after its descendants • Application: compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories AlgorithmpostOrder(v) foreachchild w of v postOrder (w) visit(v) Quiz! 9 cs16/ 8 3 7 todo.txt1K homeworks/ programs/ 4 5 6 1 2 h1c.doc3K h1nc.doc2K Robot.cpp20K DDR.cpp10K Stocks.cpp25K Trees
Comparison • Preorder • Euler Tour Traversal • Preorder: Visit a node at the first sight • Postorder: Visit a node at the last sight • Postorder B E F K I J Trees
Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal • Steps • Push the root to the stack • Pop the stack and visit it • Push the children in a reverse order (via the use of another stack) • Repeat 2) and 3) until the stack is empty See the animation in the subsequent slides! Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo A Stack Preorder: Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo B C D By using another stack Preorder: A Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo E F C D Preorder: A B Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo F C D Preorder: A B E Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo I J K C D Preorder: A B E F Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo J K C D Preorder: A B E F I Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo K C D Preorder: A B E F I J Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo C D Preorder: A B E F I J k Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo G H D Preorder: A B E F I J k C Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo H D Preorder: A B E F I J k C G Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo D Preorder: A B E F I J k C G H Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo Preorder: A B E F I J k C G H D Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Preorder Traversal: Demo Done! Preorder: A B E F I J k C G H D Trees
Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal • Steps • Push the root node to stack1 . • Pop a node from stack 1, and push it to stack 2. • Then push its children sequentially to stack 1. • Repeat step 2) and 3) until stack 1 is empty. • Pop all nodes from stack 2 to obtain the traversal in postorder. See the animation in the subsequent slides! Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo D C B A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo C B D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo H G B C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo G B H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo F E B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo K J I E F B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo J I E K F B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo I E J K F B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo E I J K F B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo E I J K F B G H C D A Stack 1 Stack 2 Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Iterative Implementation of Postorder Traversal: Demo E I J K F B G H C D A By popping all elements in stack 2 Stack 1 Stack 2 Postorder: E I J K F B G H C D A Trees
A B C D E G H F I J K Other Traversal • Breadth-first traversal (aka level-order traversal) • Idea: Visit all the nodes at depth d before visiting the nodes at depth d+1 • Implementation: Using a queue level-order traversal: A B C D E F G H I J K Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Front End Queue A Output: Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue BCD Output: A Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue CDEF Output: AB Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue DEFGH Output: ABC Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue EFGH Output: ABCD Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue FGH Output: ABCDE Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue GHIJK Output: ABCDEF Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue HIJK Output: ABCDEFG Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue IJK Output: ABCDEFGH Trees
A C D B E G H F K I J Breadth-first Traversal: Demo Queue JK Output: ABCDEFGHI Trees