Solubility Equilibrium
120 likes | 146 Views
Learn about solubility product constants (Ksp) and how they predict precipitants forming. Explore spontaneous vs. nonspontaneous reactions, entropy, and Gibbs free energy.

Solubility Equilibrium
E N D
Presentation Transcript
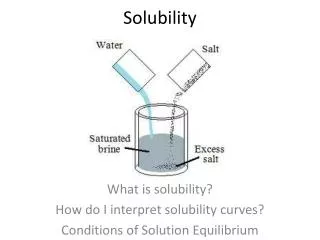
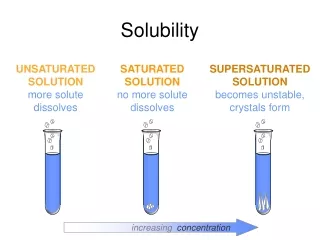
Solubility Product Constant • Ksp: solubility product constant • The product of the concentrations of the ions each raised to a power equal to the coefficient of the ion in the dissociation equation • Smaller the numerical value, lower the solubility • PbCrO4 Pb2+ + CrO42- • Ksp = [Pb2+][CrO42-]= 1.8x10-14
Predicting Precipitants • Kspcan be used to predict if precipitants will form • If the product of the concentration of the two ions in soln is greater than the Ksp, a precipitant will form • 0.50 L of 0.002M Ba(NO3)2 is mixed with 0.50L of 0.008MNa2SO4. • Insoluble compound: BaSO4 • Ksp: 1.1x10-10 (found in a chart) • [ions] are ½ because the volume was doubled • [Ba2+]x[SO42-] • (0.001M)(0.004M)=4x10-6 • 4x10-6>1.1x10-10 (Ksp) • Precipitant forms
Common Ion • Common Ion: an ion that is found in both salts and a solution. • Add lead nitrate to a saturated solution of lead chromate dec. solubility of lead chromate • Common Ion Effect: lowering solubility from addition of a common ion
Free Energy and Spontaneous Rxn. • Free Energy: energy that is available to do work • Engines ~30% efficient • Most Living things only reach 70% efficiency • Spontaneous Reaction: occurs naturally and favors the formation of products • Produce substantial amounts of products at equilibrium and release free energy • Nonspontaneous Reaction: doesn’t favor the formation of products nor give substantial amounts of products
Spontaneous and Nonspontaneous terms do not refer to reaction rates • Some spontaneous reactions go so slowly they appear nonspontaneous • Changes in temperature or pressure may be needed to determine if a reaction is spontaneous • Coupling a nonspontaneous and a spontaneous reaction can allow a nonspontaneous reaction to occur
Entropy • Measure of disorder • Law of Disorder: the natural tendency is for a system to more in the direction of maximum disorder and randomness • Increase in Entropy favors spontaneous reactions • Decreases in Entropy favors nonspontaneous reactions
The size and direction of enthalpy changes and entropy changes together determine whether a reaction is spontaneous • Favors products and free energy is releases • Spontaneous if • Exothermic: decrease enthalpy (H) • Increase entropy (S) • Nonspontaneous if: • Endothermic: increase enthalpy (H) • Decrease entropy (S)
Gibbs Free Energy • Maximum amount of energy that can be coupled to another process to do useful work. • G = H - TS • Temperature (K) • G is negative: spontaneous process • G is positive: nonspontaneous process