Hydrilla verticillata
90 likes | 408 Views
Hydrilla verticillata. Water thyme. HISTORY. Origin – Possibly Africa, Asia, India, or Austrailia Introduced into Florida 1950’s for aquarium use – dioecious strain Appeared in the Patomac drainage in the 1970’s – monecious strain

Hydrilla verticillata
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hydrilla verticillata Water thyme
HISTORY • Origin – Possibly Africa, Asia, India, or Austrailia • Introduced into Florida 1950’s for aquarium use – dioecious strain • Appeared in the Patomac drainage in the 1970’s – monecious strain • Has become the most expensive aquatic plant control project in the southeastern US
DISTRIBUTION • Since introduction, has spread to 690 bodies of water in 190 drainages in 21 states • Is present in Pennsylvania: Schuylkill River, downtown Philly Lake Nockamixon – SW Pa Highland Lake – Bradford Co.
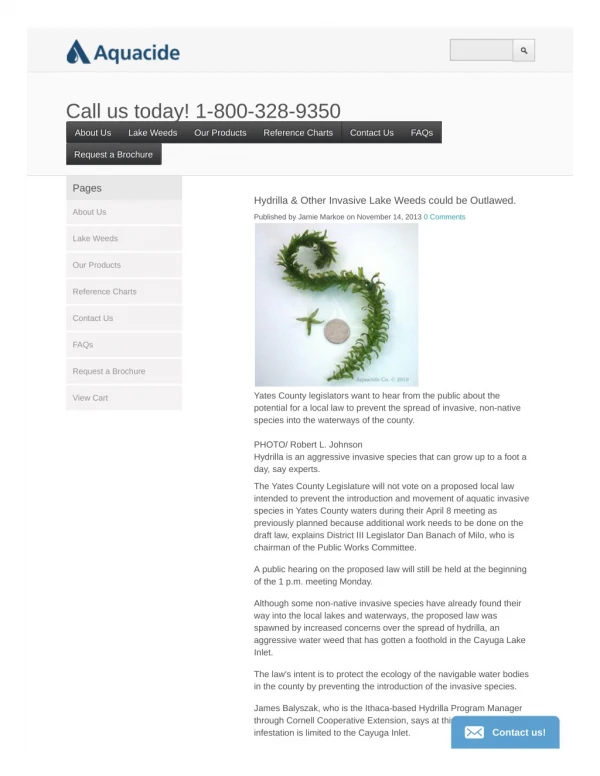
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION • 4-8 leaves in whorls around stem – leaf margins saw-toothed • Rooted – stems to 25’ long • Profuse branching at the surface • Produces both male and female flowers • Is sometimes mistaken for the native plant Elodea canadensis
GROWTH & REPRODUCTION • Prolific reproducer – broken stems, seeds, turions, and tubers • Can grow in any fresh water or sea water with a salinity of 7% • South – overwinters as perenial • North – overwinters as tuber and regrows from there • Can grow in 1% of full sunlight
CONTROL • $5 million to control 7,600ha in Florida • US Army Corps of Engineers - $1 million to suppress hydrilla in Jacksonville Distric and $400,000 to supress in Lake Seminole • Grass carp have been introduced as a control agent • Asian Hydrilla Leaf Mining Fly • Hydrilla tuber weevil
POSITIVE ASPECT • Has been discovered to be a biological remediation agent • Shown to be capable of removing dissolved lead from a waterway
REFERENCES • http://www.ecy.wa.gov/Programs/wq/plants/weeds/hydrilla.html • http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/IG120 • http://www.invasive.org/eastern/biocontrol/7Hydrilla.html • http://www.dcnr.state.pa.us/Forestry/invasivetutorial/hydrilla.htm • http://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/images/hydver/elocanc1.jpg • http://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/node/183 • http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=HYVE3 • http://nas.er.usgs.gov/taxgroup/plants/maps/Hy_verti_distr_us_Dec_03_web.JPG • http://nas.er.usgs.gov/taxgroup/plants/docs/hy_verti.html • http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=13903888 • http://www.erie.psu.edu/seagrant/publications/fs/Hydrilla.pdf