Chapter 24 World War II
2.23k likes | 2.49k Views
Chapter 24 World War II. ?? - 1945. Chapter 24 Section 1. I can list the events that led to the outbreak of World War II. Reading: Pgs. 802 - 807. Bullet Points p. 795. Bullet Points: Pg.829. Read pgs. 770 - 775. Events. 1918 – World War I Armistice was not a world wide treaty

Chapter 24 World War II
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 24World War II ?? - 1945
Chapter 24 Section 1 I can list the events that led to the outbreak of World War II
Reading: Pgs. 802 - 807 Bullet Points p. 795 Bullet Points: Pg.829 Read pgs. 770 - 775
Events • 1918 – World War I Armistice was not a world wide treaty • Germans punished and suffer from WWI • 1921 – World suffers post war recession • Adolf Hitler becomes the leader of the German Nazi Party
Different Countries With Similar Problems and Results • Russia • Italy • Germany • Japan
Italy • Economic and Social Problems cause unrest • 1922 – Benito Mussolini threatens to overthrow government How does the Italian government respond?
Italy • Mussolini named “Prime Minister” • Creates World’s First Fascist Government
Fascism • A political system based on militarism, extreme nationalism, and loyalty to the state and its leader. • The boss is always right • Superior nations must conquer and control weaker nations
Mussolini • Italy is superior to other countries • Return to the Roman Empire • Banned • Freedom of the Press • Other Political Parties • Jailed or Murdered Critics
Italy Problems Government Changes
Russia Joseph Stalin and the Communist Party
Russia • Communism created a totalitarian government in Russia • Totalitarian - Single Party System • Government controls farms, land, animals, and buisnesses • 4 million critics were executed or sent to prison camps (GULAGS)
Russia Problems Government Society
Germany • Economic struggles caused by WWI led to the rise of the Nazi Party and Adolf Hitler • Harsh treatment from WWI left many Germans unhappy with the World
Nazism • Form of Fascism • Anti-Semitic • Germans are the Master Race • Believed WWI was lost because Jews and inferior people like Gypsies • Hitler uses this belief to his advantage
Adolf Hitler • Elected Chancellor in 1933 • Political Parties Outlawed • Secret Police Enforce His Will
Jewish Community in Germany • Blamed for social and economic issues • Scapegoat • Banned from professions • Community was attacked • Sent to slave labor camps
Germany Government Society
Japan • Japan’s economy struggles following WWI • Japan felt that they need space • 1936 – Militarists take control
Japan’s Military Aggression • Believed they were superior • Racist • Aggression – Warlike actions against another nation without cause • 1931 – Japan Seizes Manchuria and China • 1937 – Attacks Nanjing China, 250,000 Civilians and POW’s killed
Japan Government Society
Consequences • Japan suspended from League of Nations for one year
Four New Powers Italy Russia Japan Germany Leaders
Italy’s Military Aggression • 1935 – Italy Invades Ethiopia • HaileSelassie (Ethiopian leader) appeals to the League of Nations • Weak response • Ethiopia Falls
Germany’s Military Aggression • Hitler rebuilds German Army • League of Nations objects • 1936 – Troops sent into Rhineland • League of Nations objects • 1938 – Hitler takes over Austria • No one does anything
German Aggression • 1938 – Germany tries to take over Czechoslovakia • Britain & France Object • Munich Pact • Britain and France agree to let Germany take part of Czechoslovakia (Sudetenland) in return for no further aggression • No one asked the Czechs
Appeasement • A policy of giving into aggression to avoid war • Neville Chamberlain (British PM) • “Peace for our time” • Did it work? • (NO.) 1939 – Hitler takes the rest of Czech
America’s Response • 1935: Neutrality Act • No assistance to those in war • Good Neighbor Policy • US removes troops from Latin America • Why did we engage in the Neutrality Act and the Good Neighbor Policy?
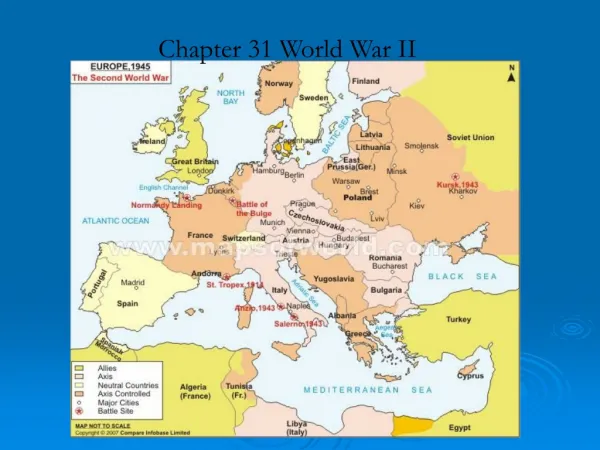
War Begins in Europe • Britain and France promise Poland they will come to their aid if Germany invades… • Aug. 1939: Hitler and Stalin agree to non-aggression deal (even though they’re enemies??) • Secretly agree to divide up Poland
War Begins in Europe • Sept. 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland • September 3, 1939: France and England declare war on Germany • Sept. 17, 1939: Russia invades Eastern Poland and later Finland • Russia also, annexed Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia
Germany’s March • April-May 1940: • Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Luxemburg, and Belgium Fall • France falls under attack (May 1940)
Fight for France • Britain sends troops to help France • British and French put on the defensive • Germans pushed them back to Dunkirk (French port on the English Channel) • Britain sends all ships to rescue soldiers • With no one in his path, Hitler marches to Paris (the capital of France)
June 22, 1940 France Surrenders Barely six weeks after Germany invaded
Battle for Britain • Britain stands alone • Winston Churchill, the (new) British Prime Minister rallies the country: “…Even though large tracts of Europe and many old and famous States have fallen or may fall into the grip of the Gestapo and all the odious apparatus of Nazi rule, we shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end… We shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender…”