Protein Synthesis
500 likes | 724 Views
Protein Synthesis. sugar. sugar. sugar. sugar. N base. N base. N base. N base. phosphate. phosphate. phosphate. phosphate. Nucleotide chains. Nucleic acids __________________________________________________________ DNA double-sided double helix ______________ RNA single-sided

Protein Synthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
sugar sugar sugar sugar N base N base N base N base phosphate phosphate phosphate phosphate Nucleotide chains • Nucleic acids • __________________________________________________________ • DNA • double-sided • double helix • ______________ • RNA • single-sided • ______________
O O=P-O O 5 CH2 O N C1 C4 C3 C2 RNA Nucleotide
3 differences from DNA • Single strand instead of double strand • __________________________ • __________________________
Types of RNA • ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Types of RNA Ribosome • _______________________________________________________________ Ribosomal RNA
tRNA (transfer RNA) • Cross-like shape • At one end _________________ ____________________________ • At the other end ____________ ____________________________ • Acts like a truck (carrying amino acids)
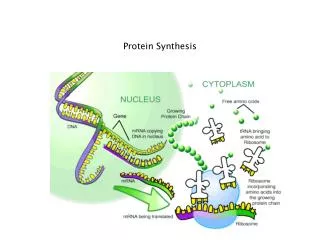
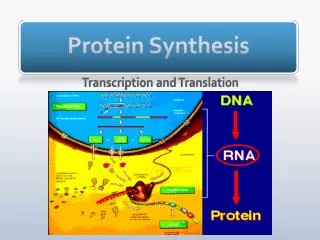
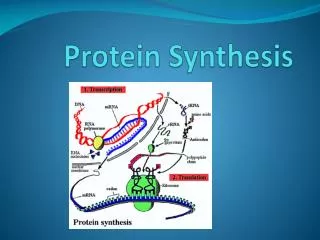
1d. Know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa From gene to protein
Transcription - _______________________________________________ Translation - _________________________________________________
Transcription From __________________________ To __________________________
TRANSCRIPTION • Occurs in the ___________________. • DNA is copied into mRNA with the aid of an _________________ ________________________ Transcription
mRNA (messenger) • Copies genetic code of DNA by ________________________. • DNA info then get passed down to mRNA (_________________________)
Codons (on mRNA) • A three letter “word” that _______________________________.
_______________ A segment of DNA in eukaryotes that codes for a ____________________ _______________ A segment of DNA that ___________________________ Exons and Introns DNA
Eukaryotic RNA Editing Exon Intron DNA • The introns are _______________________. • The exons are _________ _______________________ _______________________. Pre-mRNA mRNA Cap Tail
4a. Know the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA.
Translation From __________________________ To __________________________
During protein construction, _____________ _________________ transfers each _______________ to the ____________________. • Transfer RNA (tRNA)- collects __________________ __________________________ • _______________________-a sequence of 3 bases that are _____________________ _________________________ _________________________
Amino Acids • ___________________________________ ___________________________________ • At least one kind of tRNA is present for each of the 20 amino acids used in protein synthesis. AGU
Protein Synthesis • _______________ = reading the mRNA info to form _____ _________________ _________________. • Occurs on _______
Translation • The ribosome binds _____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________. Lysine Phenylalanine tRNA Methionine Ribosome mRNA Start codon
Lysine • Continued Protein Synthesis tRNA Translation direction mRNA Ribosome
The process continues until the _____________________________ ___________________________________________________________. Polypeptide Ribosome tRNA mRNA
4b. Know to apply the genetic coding rules to predict the sequence of amino acids from a sequence of codons in RNA.
Genetic code • The genetic codes build all the proteins in our body using 20 different amino acids. • How many 3 letter words can you make from the letters A,T,G and C? • Answer: ____________
Make mRNA • DNA sequence TAC TTT TTG TTC CAT ATC • mRNA sequence ___________________________
Make Protein • mRNA sequence AUG AAA AAC AAG GUA UAG • Amino Acid sequence ____________________________
Central Dogma DNA AGT CCA GCT ________ _____________ mRNA ________________ ________ tRNA AGU CCA GCU ___________ ____________ Amino Acid ________________ ____________ Chain
4e. Know proteins can differ from one another in the number & sequence of amino acids.
Mutation • A mistake in DNA replication is called a _____________________. • ________: An agent, such as a chemical, ultraviolet light, or a radioactive element, that can induce or increase the frequency of mutation in an organism.
Mutations • Some mutations can: • Have little to no effect • _______________________ (produce organisms that are better suited to their environments) • Be deleterious (harmful)
Point mutation leads to Sickle cell anemia What kind of mutation?
Sickle cell anemia • Primarily _________________ • recessive inheritance pattern • strikes 1 out of 400 African Americans
Mutations • Can be either ___________________________________ mutations. • Point mutations = a change in a ________________________ in a sequence of DNA.
Mutations • Types of mutations • _______________________________: the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is __________ _________________, so that every codon beyond the point of insertion or deletion is read incorrectly during translation. OUR BIG DOG BIT THE MAN OBU RBI GDO GBI TTH EMA N ORB IGD OGB ITT HEM AN
Frameshift Mutation • ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
Mutations • Types of mutations • ______________________: an entire section of DNA is reversed. • Ex. hemophilia, ______________________