Functional components of a computer
350 likes | 828 Views
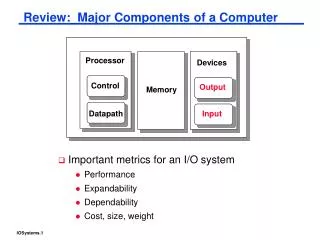
Functional components of a computer. Main memory. CPU. Arithmetic/Logic Unit ( ALU ). Control Unit. Register(s). Registers. The special storage devices in the CPU that CPU uses over and over again for execution of stored-program instructions. There are two types of registers :

Functional components of a computer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Main memory CPU Arithmetic/Logic Unit ( ALU ) Control Unit Register(s)
Registers • The special storage devices in the CPU that CPU uses over and over again for execution of stored-program instructions. • There are two types of registers : • General purpose registers • Special purpose registers
Registers Examples of special purpose registers : • PC ( Program Counter ) • IR ( Instruction Register ) • MAR ( Memory Address Register ) • MDR or MBR ( Memory Data Register or Memory Buffer Register ) • PSW ( Program Status Word ) • etc.
Main Memory CPU R0 MDR R1 IR PC MAR RN Control unit ALU Data bus Control bus Address bus
Registers • MBR: Memory Buffer Register • เป็นหน่วยเก็บข้อมูลที่จะส่งออกไปเก็บหรือที่ดึงมาจากหน่วยความจำ • MAR: Memory Address Register • เป็นตัวกำหนดแอ็ดเดรสของหน่วยความจำที่ MBR จะทำการอ่านหรือเก็บข้อมูล • IR: Instruction Register • เป็นส่วนที่เก็บคำสั่ง(Opcode) ที่จะถูกเรียกใช้งาน • PC: Program Counter • เป็นส่วนที่เก็บแอ็ดเดรสของคำสั่งถัดไปที่จะถูกดึงออกมาจากหน่วยความจำหลัก • AC: Accumulator • จะใช้ในการเก็บค่าชั่วคราวของโอเปอแรนด์(operands)และผลลัพธ์ของการคำนวณในส่วนALU
Main Memory Operations Memory read operation • Transfers the content of a specific main memory location to the CPU. • The content of the main memory location remains (unchanged).
Main Memory Operations Memory write operation • Transfers a word of information from the CPU to a specific main memory location. • Destroys the former content of the main memory location. Memory access time • The time it takes to perform a memory read or a memory write operation.
วิธีการเข้าถึงข้อมูล(Access Method) • การเข้าถึงแบบลำดับ (Sequential Access) • การเข้าถึงจะช้าเพราะต้องสแกนหาตำแหน่งที่ต้องการทีละเรกคอร์ด • เทปแม่เหล็ก • การเข้าถึงแบบโดยตรง (Direct Access) • การเข้าถึงจะเร็วเพราะหัวอ่าน/บันทึกข้อมูลสามารถเข้าถึงข้อมูลได้โดยตรง • ฮาร์ดดิสก์ • การเข้าถึงแบบสุ่ม (Random Access) • การเข้าถึงจะเร็วและเวลาในการเข้าถึงข้อมูล ณ ตำแหน่งใดๆ จะคงที่ • หน่วยความจำหลัก, แคช
โครงสร้างของคำสั่ง 0 34 15 opcode Address 0001คือ โหลด(นำ)ข้อมูลจากหน่วยความจำมาเก็บไว้ที่AC 0010 คือ นำข้อมูลที่อยู่ในACมาบันทึกไว้ที่หน่วยความจำ 0101 คือ บวกค่าจากหน่วยความจำเข้ากับค่าที่อยู่ในAC
Memory CPU Registers PC 3 0 0 300 301 302 940 941 5 9 4 1 2 9 4 1 0 0 0 2 1 9 4 0 0 0 0 3 AC IR 1 9 4 0 : : 16 bits Step 1 • PC (Program Counter) บรรจุตำแหน่งของหน่วยความจำ(=30016) • Processor ดึงคำสั่ง (194016)ในหน่วยความจำตำแหน่งที่ 30016 เข้ามาเก็บไว้ที่ IR • PC เพิ่มค่าขึ้น 1 ตำแหน่ง
PC 3 0 1 300 301 302 940 941 0 0 0 3 2 9 4 1 0 0 0 2 1 9 4 0 5 9 4 1 IR 1 9 4 0 16 bits Memory CPU Registers AC 0 0 0 3 : : 00012 = 116 Step 2 • Processor เรียกใช้คำสั่ง (194016) ใน IR • 4 bits แรกคือคำสั่งให้ load ข้อมูลที่อยู่ที่ตำแหน่ง 94016
PC 3 0 1 300 301 302 940 941 0 0 0 3 2 9 4 1 0 0 0 2 1 9 4 0 5 9 4 1 AC 0 0 0 3 IR 5 9 4 1 16 bits Memory CPU Registers : : Step 3 • คำสั่งถัดไป (594116)ที่อยู่ที่หน่วยความจำตำแหน่งที่ 30116ถูกนำเข้ามาเก็บไว้ที่ IR • PC เพิ่มค่าขึ้น 1 ตำแหน่ง
PC 3 0 2 300 301 941 302 940 0 0 0 2 1 9 4 0 2 9 4 1 5 9 4 1 0 0 0 3 IR 5 9 4 1 01012 = 516 16 bits Memory CPU Registers AC 0 0 0 5 : : 3+2 = 5 Step 4 • ทำตามคำสั่ง (594116 ) • 516 = 01012เป็นคำสั่งให้บวกค่าของข้อมูลที่อยู่ในหน่วยความจำตำแหน่งที่ 94116กับค่าที่เก็บไว้ที่ AC และให้นำผลลัพธ์ที่ได้ไปเก็บไว้ที่ AC
PC 3 0 2 941 300 301 302 940 5 9 4 1 2 9 4 1 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 2 1 9 4 0 AC 0 0 0 5 IR 2 9 4 1 16 bits Memory CPU Registers : : Step 5 • คำสั่งถัดไป (294116) ที่อยู่ที่หน่วยความจำตำแหน่งที่ 30216ถูกนำเข้ามาเก็บไว้ที่ IR • PC เพิ่มค่าขึ้น 1 ตำแหน่ง
PC 3 0 3 300 301 302 940 941 0 0 0 3 2 9 4 1 0 0 0 5 1 9 4 0 5 9 4 1 IR 2 9 4 1 00102 = 216 16 bits Memory CPU Registers AC 0 0 0 5 : : Step 6 • ทำตามคำสั่ง (294116 ) • 216 = 00102เป็นคำสั่งให้บันทึกค่าข้อมูลที่อยู่ใน AC ลงในหน่วยความจำตำแหน่งที่ 94116