Blood and Plasma
200 likes | 488 Views
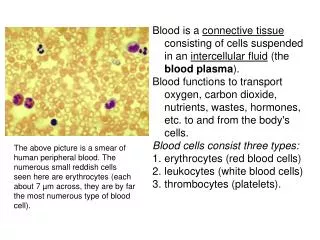
Blood and Plasma. Prof. K. Sivapalan. Blood – introduction. Blood is a liquid tissue. It has different types of cells. Intercellular substance is Plasma. There are no tight junctions, collagen, and hyaluronic acid. Composition of the blood. Plasma: Serum + fibrinogen. Cells

Blood and Plasma
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Blood and Plasma Prof. K. Sivapalan
Blood – introduction. • Blood is a liquid tissue. • It has different types of cells. • Intercellular substance is Plasma. • There are no tight junctions, collagen, and hyaluronic acid. Blood and plasma
Composition of the blood. • Plasma: • Serum + fibrinogen. • Cells • Red blood cells (erythrocytes) • White blood cells (leucocytes). • Neurtophil, eosinophil, basophil, monocyte, lymphocyte. • Platelets. Blood and plasma
Physical properties. • Color- red. [hemoglobin] • Osmolality: 290 – 300 m osmol/L. • Osmotic pressure: 5000 mm Hg. [≈7 Atm] • Colloid osmotic pressure [oncotic pressure] : 25 mm. Hg. • Viscosity: 3 – 4 times that of water. • Specific gravity: 1.050 – 1.060. Blood and plasma
Functions of Blood • Transport of, • Water. • Oxygen. • Nutrients: • Glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, iron, calcium, etc. • Wastes: • Urea, carbon dioxide, bilirubin, heat, acid. • Hormones: • Water soluble, • fat soluble. Blood and plasma
FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD-ctd.. • Microcirculation. • Hemostasis. • Platelets, fibrinogen and clotting factors. • Immunity. • Antibodies, white blood cells. Blood and plasma
BLOOD VOLUME. • Blood : 8 % of the body weight. • 80 ml / Kg ± 10 % • Plasma: 5 % of the body weight. • Males 5-6, females 4-5 liters. • Distribution in the vessels: • Lungs- 20 % [1 Liter.] • Veins- 60 % [3 Liters.] • Heart, Arteries, capillaries: • 20 % [1 Liter.] Blood and plasma
Distribution in Detail. Blood and plasma
Measurement. • Dilution method. • V1C1 = V2C2. • Plasma volume. • Evans blue, Rose Bengal, Vital Red, Radioactive Iodine etc. • Blood volume. • Red Cells labeled with Radio active Chromium. Blood and plasma
Factors that Affect Blood Volume. • ECF volume- Sodium ions Dehydration. Water Balance. • Blood loss. Blood and plasma
Control of Blood Volume. • Circulatory mechanism • Volume receptor mechanism. • Renin - Angiotensin – Aldesterone mechanism. • Atrial Natriuretic Peptide. Blood and plasma
Circulatory Mechanism • Blood volume determines cardiac output. • Cardiac output determines blood pressure. • Blood pressure determines Urine production. • Urine production determines ECF volume and blood volume. Blood and plasma
Volume Receptor Mechanism. Volume receptors in RA and IVC. [stimulated by stretch which represents blood volume] + [ ↑ impulses in afferents with volume] - Decreased blood volume. Post. Pituitary through Hypothalamus. • [Reabsorption of water ↓, ↑Urine out put] - [ ↓secretion.] Collecting ducts in Kidney. Anti Diuretic Hormone. Blood and plasma
Renin - Angiotensin – Aldesterone Mechanism. • Renin is secreted by the Juxta Glomerular Cells in response to low sodium in tubule and low blood pressure in afferent arterioles. • It converts angeotensinogen into angeotensin I which in turn gets converted to angeotensin II. • Angeotensin stimulates secretion of Aldesteron. • Aldesteron stimulates sodium re-absorption in distal tubule. • Keeps blood volume due to osmotic force. Blood and plasma
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide. • Stretch of the right atrium is determined by venus return which mainly depends on blood volume. • ANP is secreted by Right Atrium in response to stretch. • ANP causes Sodium and water loss in urine. Blood and plasma
Properties of plasma. • Straw color. • Volume - 3.5 liters. • High Viscosity. • Osmolality- 290 m Osmols/L • Specific gravity- 1.025. • Coagulability. Blood and plasma
Composition of PLASMA. • Proteins- 7.5 g/100 ml. (dL) • Albumin. 4.5 g. • Globulin. 2.5 g. • Fibrinogen. 0.3 g. • [source: liver, plasma cells.] • Electrolytes. • Nutrients. • Hormones. • Waste products. Blood and plasma
Functions of plasma. • Fluid exchange. • Maintenance of pH- Buffering. • Transport of substances. • Hemostasis- Clotting. • Immunity. • Reserve of body proteins. Blood and plasma
MEASUREMENT OF VISCOSITY. • Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate. • Height of clear plasma at the end of the first hour of standing. • Determinants of ESR: • VISCOSITY of plasma. • ROULEAUX formation. • Westegran tube in ESR stand. • VISCOMETER. Blood and plasma