Mendelian Genetics
110 likes | 303 Views
Mendelian Genetics. Gregor Johann Mendel. 1822-1884 Austrian “Father of Modern Genetics” http://www.biography.com/people/gregor-mendel-39282. Inheritance. What is the difference between a characteristic and a trait ? Give examples of each.

Mendelian Genetics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Gregor Johann Mendel • 1822-1884 • Austrian • “Father of Modern Genetics” • http://www.biography.com/people/gregor-mendel-39282
Inheritance • What is the difference between a characteristic and a trait? • Give examples of each. • Up until Mendel, the prevailing theory of inheritance was that the traits of offspring are “blends” of the parents • A plant with red flowers crossed with a plant with white flowers would give offspring with pink flowers
Mendel’s Experiments • Between 1856 and 1863, working as a schoolteacher in a monastery, Mendel grew and tested over 29,000 pea plants looking at the inheritance of traits • Picked characteristics that had 2 distinct traits • Performed simple crosses in which the plants differed in only one trait • Monohybrid cross
True-breeding • What was Mendel’s definition of true-breeding? What do we now call true-breeding?
Generations • P generation: parental • F1 generation: first filial generation • Filial: related to your offspring • F2 generation: second filial generation • How is the F1 related to the F2 generation? • How is the P generation relation to the F2 generation?
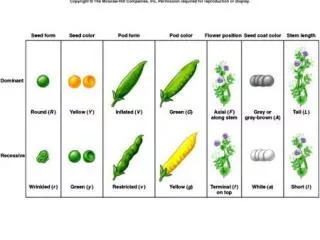
Mendel’s results • Performed many different monohybrid crosses and always found the 3:1 ratio of traits in the F2 generation • Flower color • Seed shape • Seed color • Pod shape • Pod color • Flower position • Stem length (height)
Mendel’s Conclusions • The trait he saw expressed in the F1 generation he described as dominant • The trait that is masked in the F1 and reappears in the F2 is the recessive
Mendel’s Conclusions • Law of Segregation • Be able to explain the two parts of the law of segregation.
Genes and Alleles • Since there are two copies of each chromosome in somatic cells, it means there are two copies of each gene • Allele: