Multispectral Remote Sensing Systems
510 likes | 1.15k Views
Multispectral Remote Sensing Systems. Landsat SPOT Weather satellites - GOES - AVHRR High-resolution satellite - IKONOS Hyper-spectral sensor - AVIRIS EOS-Terra instruments - ASTER - MODIS. Landsat Program.

Multispectral Remote Sensing Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Multispectral Remote Sensing Systems Landsat SPOT Weather satellites - GOES - AVHRR High-resolution satellite - IKONOS Hyper-spectral sensor - AVIRIS EOS-Terra instruments - ASTER - MODIS
Landsat Program • Originally called (ERTS) - Earth Resources Technology Satellite. • First satellite launched in 1972 • Broad scale repetitive surveys of the landscape • Visible, NIR spectral bands (Landsats 1,2,3), and MIR and Thermal (Landsats 4 and 5) Sensors: • Multispectral scanner (MSS) • Return beam vidicon (RBV) • Thematic Mapper (TM) • Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+)
Chronological Launch and Retirement History of the Landsat Satellite Series
Inclination of the Landsat Orbit to Maintain A Sun-synchronous Orbit Inclination = 98.2degree
Orbit Tracks of Landsat 1, 2, or 3 During A Single Day of Coverage
Landsat 4 and 5 Platform with Associated Sensor and Telecommunication Systems
Spectral and Spatial Resolution of the Landsat Multispectral Scanner (MSS), Landsat 4 and 5 Thematic Mapper (TM), Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+), SPOT 1, 2, and 3 High Resolution Visible (HRV), and SPOT 4 High Resolution Visible Infrared (HRVIR) Sensor Systems
Seven Bands of Landsat Thematic Mapper Data of Charleston, SC, Obtained on February 3, 1994
Landsat 7 Image of Palm Spring, CA 30 x 30 m (bands 4,3,2 = RGB)
Landsat 7 Image of Palm Spring, CA 30 x 30 m (bands 7,4,2 = RGB)
Chronological Launch History of the SPOT Satellites Sensor: SPOT 1,2,3: HRV (High Resolution Visible) SPOT 4: HRVIR(High Resolution Visible and Infrared)
SPOT NADIR View 60 km swath width 3 km overlap 117 km total width
Comparison of the Detail of 30 x 30 m Landsat TM Band 3 Data and SPOT 10 x 10 m Panchromatic Data of Charleston, SC Courtesy of SPOT Image, Inc.
Geographic Coverage of the SPOT HRV and Landsat Thematic Mapper Remote Sensing Systems
Weather Satellites and Sensors • Examples: • (1) GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) • (2) NOAA AVHRR (Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer)
GOES Hurricane Image GOES
GOES East Coverage GOES East Infrared August 25, 1989 GOES East Visible August 25, 1989
Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Data Acquisition Characteristics • Visible, NIR, Thermal • 1.1 km Resolution - local area coverage (LAC) • 4 km Resolution - global area coverage (GAC) • Used for meteorological studies • Vegetation pattern analysis • Gaining popularity for global modeling • Broad spectral bands • Not ideally suited for vegetation but used to determine • general patterns.
Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Mosaic of the Conterminous United States
Global Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Image Produced Using Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Imagery
High Spatial Resolution Sensor: IKONOS http://www.spaceimaging.com IKONOS Panchromatic Images of Washington, DC 1 x 1 m spatial resolution Panchromatic: 1m MX: 4m
IKONOS Panchromatic Stereopair of Columbia, SC Airport November 15, 2000
IKONOS Imagery of Columbia, SC Obtained on October 28, 2000 Panchromatic 1 x 1 m Pan-sharpened multispectral 4 x 4 m
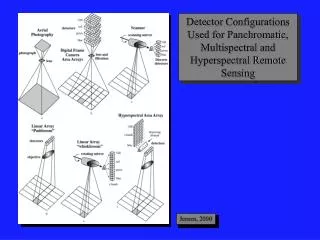
Hyper-spectral Remote Sensing: Imaging Spectrometry
Hyper-spectral Sensor NASA AVIRIS: Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer
Earth Observing System - Terra Instruments ASTER - Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer CERES - Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System MISR - Multi-angle Imaging Spectroradiometer MODIS - Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer MOPITT - Measurement of Pollution in the Troposphere
Earth Observing System - Terra Instruments MODIS - Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Spectral Range 0.4 - 14.4 mm Spatial Resolution 250 m (2 bands), 500 m (5 bands), 1000 m (29 bands) ASTER - Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer Spectral Range VNIR 0.4 - 14.4 mm, SWIR 1.6 - 2.5 mm, TIR 8 - 12 mm Spatial Resolution 15 m (VNIR : 3 bands) 30 m (SWIR: 6 bands) 90 m (TIR: 5 bands)
EOS Data Gateway (Free data) http://edcimswww.cr.usgs.gov/pub/imswelcome/