Exploring Energy: Sources and Production Methods
500 likes | 615 Views
Learn about harnessing energy to power homes, run machines, and fuel transportation. Discover forms of energy and electricity production. Understand atoms, isotopes, and radiation in power generation. Explore background radiation sources and health effects from exposure.

Exploring Energy: Sources and Production Methods
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Harnessed Atom Unit 1 Lesson 1
We Use Energy to: • Power factories & businesses • Heat & Light Homes and Schools • Run appliances & machines • Fuel Cars, Airplanes, Trains & Ships • Run Televisions & Games • Use Telephones & Computers • Make Food & Clothing
Types of Energy Potential Kinetic
Forms of Energy • Mechanical • Chemical • Thermal • Electrical • Radiant • Nuclear
Ultimate Source of Energy • The Sun • Photosynthesis • Heat • Air Currents • Ocean Currents
Primary Sources of Energy • Fossil Fuels • Geothermal • Nuclear • Solar • Tidal/Water
Efficiency • Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed • Energy Conversions are Inefficient – someleaves as heat • Energy Conservation extends life of a resource
The Harnessed Atom Unit 1 Lesson 2
What is Electricity? • The flow of electrons- as in a wire • Static – as when you comb your hair • Our most versatile and adaptable form of energy
Electricity Production • By converting one source of energy into heat • Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas) • Uranium • Water • Solar • Wind • Biomass • Geothermal
Electricity Production • Heat up Water to make Steam • Steam turns a Turbine • Turbine moves a Magnet through a coil of Wire • Magnetic Field causes the e- to move
How do we Move Electricity • About 1000 Utilities • Build Plants • String /Bury Wire • Fuel for plants • Meters on houses & businesses
Utilities • Cover a specific region • Are Regulated • It’s essential • Must provide as needed • Must provide amt. needed • Charge fair rates • Build based on Prediction of Usage
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 1
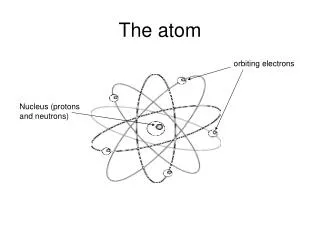
Atom • 92 different natural atoms • Elements are different kinds of atoms • Combining different atoms makes molecules • Combined during a chemical reaction • Building blocks of the universe
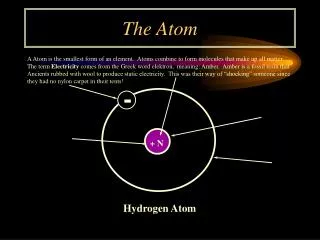
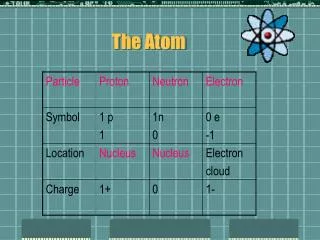
Atoms • Nucleus • Protons – positive charge • Identify the Atom • Neutrons – no charge • Electrons • Negative charge • Move around Nucleus • #Protons = #Electrons • Balanced charge
Isotope • Same type of atom, different number of neutrons • All atoms are isotopes • Have the same chemical properties • Name + mass • U-235 or Uranium-235
Isotope Stability • Some Proton/Neutron ratios more stable than others • Stabilize themselves by emitting radiationCalled Radioactive Decay • Energy • Particles
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 2
Radiation • Radioactive Decay • Unstable Isotopes seek to be more stable • Release energy & particles • Radiation • Energy or • Particles released • Radioactive • Substance giving off radiation
Radiation Types • Alpha • Tiny bits of atoms • Stopped by paper • Beta • Smaller particles • Stopped by aluminum foil • Gamma • Electromagnetic wave • Fast & Strong • Stopped by cement or steel
Ionizing Radiation • Alpha, Beta and Gamma • Can Change the chemical make up of things • Exposure can be dangerous • Shields are used to stop • Mechanical hands & robots
Half-Life • Decay at Random • Eventually decay to a stable element • Decay Chain – transformation into different elements before becoming stable • Half Life • Amount of time for a given isotope to lose half of its radioactivity
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 3
Recognizing Radiation • Cannot see, hear, touch or smell it • Ionizing Radiation • Knocks e- off atoms • These atoms become + • Geiger Counters sense tiny electrical changes • Photographic film badges record radiation
Warnings • Doors where radioactive materials are used or stored • Boxes & Containers • Same laws require labeling of: • Poisons, • explosives, • flammables, • combustibles
Radiation Dose • Radiation Dose – depends on • Time exposed • Amount of shielding • Distance from source • Reduce Radiation Dose • Decrease time • Decrease distance • Increase shielding
Exposure • Most people receive 150-200 millirems /year • Low Level - <5,000millirems • No effects at 50,000millirems • At low levels the body repairs itself • Radiation Sickness>100,000millirems • Death>500,000millirems
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 4
Background Radiation • Sources • Ocean • Mountains/Ground • Potassium • Thorium • uranium • Air • Food • Space (gamma)
Uranium Deposits • New Mexico • Nevada • Utah • Wyoming • Colorado • India • Brazil
Building Materials • Materials such as: • Bricks • Wood • Stone • Brick Homes50-100millirems/yr • Wooden Homes30-50millirems/yr
Cosmic Radiation • Screened by clouds & air • Higher altitudes receive more than lower altitudes • Air Plane trip4 millirems
Organisms • Plants & Animals made of radioactive elements • Food & Drink 25 millirems • Bananas & Brazil Nuts have more
Man Made sources • Medical / Dental sources • Building Materials • Nuclear Industry • Coal Fired Power Plants • Nuclear Weapons testing • Avg. 80 millirems/yr
SC Average Background Radiation • Manmade radiation level80 millirems • Natural radiation level107 millirems • Total = 187 millirems
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 5
Medical Uses • Cancer Treatment • Gamma Radiation to kill cancer cells • X-rays (em waves) • black & white picture of dense areas • CAT Scanners • color pictures of inside our bodies • Scintillation Counter • image of chemical reactions • using radioactive tracer given the patient • Labeling • Tracers to follow things in our body
Science Uses Radioactive Tracers in • Size of oil fields • Track Ocean Currents • Air & Water • Pollution Paths • Nutrient Cycles • Plants & Animals • Pollution paths • Nutrient paths
Science Uses • Dating Ancient Objects • All living things take in Carbon • Carbon-14 is a natural isotope • When organisms die, they no longer take in C • C-14 begins to decay • Half-life of C-14 is 5,760yrs • Measure difference of C-14 in old and new object • Uranium, Rubidium and Potassium used for older objects
Crime Solving • Activation Analysis • Evidence is exposed to radiation • Some of the elements will be activated • Exact chemical signature can be read
Industrial Uses • Agricultural uses • Create disease resistant/ fast growing plants • Control Insects by sterilizing males • Irradiation • Kills germs without making the object radioactive • Food • Medical Equipment
Industrial Uses • Control thickness of: • Glues • Paper • Plastic • Foil • Fill sensors for Cartons & boxes • Check Contents of Containers or Luggage
Industrial Uses • Radiography – x-rays • To find defects in metals & welds • Flow of fluid in hydraulics • Rate of wearing out • Blending of metals • Energy for • Pacemakers • Lights on runways & buoys • Power space craft
The Harnessed Atom Unit 2 Lesson 6
Fission • Fission • Splitting of an atom • Releases energy / heat • End with two new smaller elements • 2 or 3 neutrons released
Fission • Chain Reaction • One neutron splits one atom & releases 3 neutrons • 3 neutrons split three atoms & release 9 neutrons • And so on and so on
Fusion • Two atoms are joined together • Energy / heat is released • Deuterium & Tritium combine to make Helium • Neutron released • Ex. The Sun
Fusion – on earth • Magnetic field to confine H isotopes • Heat to 100mil oC • H becomes a Plasma • Electricity alters it • Magnetism molds it • 1 gal Seawater = 300 gal Gas