Chapter 8
350 likes | 608 Views
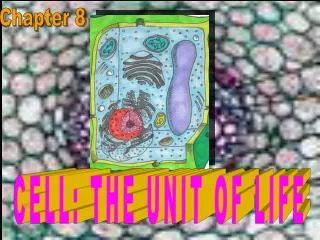
Chapter 8. CELL: THE UNIT OF LIFE. G N RAMACHANDRAN (1922--2001). Keralite, from Cochin Outstanding figure in the field of protein structure Founder of Madras School. cell. Basic Unit of Life--functional structure and fundamental unit. Multicellular. Unicellular. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek-

Chapter 8
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 8 CELL: THE UNIT OF LIFE
G N RAMACHANDRAN (1922--2001) Keralite, from Cochin Outstanding figure in the field of protein structure Founder of Madras School
cell Basic Unit of Life--functional structure and fundamental unit Multicellular Unicellular
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek- first discovered living cell Robert Brown- discovered nucleus
Schleiden and Schwann Cell Theory • All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. • All cells arise from pre-existing cells Rudolf Virchow
overview of cell -Eukaryotic- with true nucleus • Prokaryotic- with no definite nucleus
Size of cells Mycoplasma- 0.3µm in length Bacteria-3 to 5 µm in length Ostrich egg- largest single cell Human red blood cells- 7.0 µm in length Nerve cells- longest cells
Shape of cells Disc like Polygonal Cuboid Columnar Irregular Thread like
Prokaryotic Cell PPLO Bacteria mycoplasma blue green algae
Cell envolope and its modifications of prokaryotic cells Have chemically complex cell envolope- outer glycocalyx, cell wall and plasma membrane Gram positive bacteria- takes stain gram negative bacteria- does not take up stain Glycocalyx may be loose- slime layer; if thick- capsule Mesosomes In cyanobacteria- chromatophores: pigments
Cell envolope and its modifications of prokaryotic cells Bacteria may be motile or non-motile Flagellum is the organ for motion : filament, hook and basal body Pili and fimbriae- small bristle like fibres: helps in attachment and reproduction
Ribosomes and inclusion bodies of prokaryotic cells Ribosomes are 70s types with 50s and 30s subunits: sites of protein synthesis Ribosomes attached to mRNA form chains called polyribosome or poly some Inclusion bodies: are reserve food materials like phosphate granules, Cyanophycean granules and glycogen granules.
EUKARYOTIC CELLS • Protists, plants, animals and fungi • Membrane bound organelles- compartmentalization of cytoplasm • Organised nucleus with nuclear envolope. • Have a variety of complex locomotary and cytoskeletal structures. • Genetic material is organised into chromosomes
Cell wall, plastids and vacoule are present Cell wall, plastids and vacoule are absent Centrioles present Plant cell and animal cell
Cell membrane • Composed of lipids and proteins • Lipids • ( phosphoglycerides) arranged with polar heads towards the outer side and hydrophobic tails towards the inner part. • Proteins are integral proteins and peripheral proteins • Peripheral proteins; lie on the surface of membrane • Integral proteins: partially or totally buried in the membrane
Cell membrane fluid mosaic model Singer and Nicolson
Cell membrane Molecules are transported across membrane actively or passively – passive ( no energy is utilised): Water moves from higher concentration to lower concentration – Active ( using energy) Na, K etc are transported from lower concentration to higher concentration
Cell wall • Non living and rigid • Gives shape to cell, protects and helps in cell to cell interaction • Made up of cellulose / galactose/ hemicellulose etc • Middle lamella with calcium pectate holds different neighbouring cells • Plasmodesmata connects cytoplasms of nearby cells
Endomembrane system Includes endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes and vacoules Their functions are coordinated
Endomembrane system endoplasmic reticulum(ER) Smooth ER- ER with no ribosomes attached- site of synthesis of lipid Network of tiny tubular structures scattered in the cytoplasm Rough ER- ER with ribosomes attached– found in cells actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion
Endomembrane system Golgy apparatus • Camillo Golgi- first observed golgy apparatus • Disc shaped sacs or cisternae stacked parallel • Performs the function of packaging materials to be delivered Inside the cell or outside • Important site of formation of glycoproteins and gycolipids
Endomembrane system Lysosomes • Membrane bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in golgi apparatus • Rich in hydrolytic enzymes
Endomembrane system Vacuoles • Membrane bound space in the cytoplasm: contains water, sap, excretory Product and other materials • Bounded by tonoplast • In amoeba contractile vacuole is important for exretion • Food vacuole is seen in protists
Mitochondria Sausage shaped or cylindrical Double membrane structure with outer and inner membrane The inner compartment is called matrix The folding of inner membrane is called cristae Sites of aerobic respiration, called power house of cell producing ATP Autonomous body divide by fission
Plastids Bear pigments- classified intochloroplast, chromoplastandleucoplast Found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. Chloroplast: with chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments- green in colour Chromoplast- with carotene, xanthophylls- yellow, orange or red colour Leucoplast- colourless with stored nutrients: Amyloplast- store carbohydrate Elaiplasts- store oil Aleuroplast- store protein
chloroplast Mostly found in the mesophyll cells of leaves. Lens shaped, oval, spherical, etc. Double membrane structure. The inner space is called stroma Stroma consists of enzymes requred for the synthesis of carbohydrates And proteins. Stacked membranous sacs- thylakoids- grana Autonomous body
Ribosomes Granular structures – first observed by Palade (1953) Composed of ribonucleic acid and protiens- no membrane Eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S ; Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S
Cytoskeleton An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures Mechanical support, motility, maintenance of the shape of the cell
Cilia and flagella Cilia are small while flagella are large: causes movement Hair like outgrowths Shows 9+2 arrangement of microtubules 9 pairs of tubules are peripheral; 1 pair of tubules are central
Centrosome and centrioles Centrosome:Organelle containing two cylindrical structures called centrioles Centrioles form the basal body of cilia and flagella and spindle fibres Made up of nine evenly spaced peipheral fibrils of tubulin protein
Nucleus Flemming: gave the name chromatin First described by Robert Brown Nuclei Perinuclear space nucleoplasm Nucleolus is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis
Nucleus... Chromosomes During cell division chromatin reticulum condenses to form chromosomes
Nucleus... Chromosomes Types of chromosomes
Microbodies Membrane bound minute vesicles containing enzymes.